Tag: Visual edit |
m (Reverted edits by TMK3242 (talk) to last revision by Rex KingYT) Tag: Rollback |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Tabs| |
||
| − | {{Italictitle}} |
||
| + | {{Tabs2|{{BASEPAGENAME}}|Introduction}} |
||
| + | {{Tabs1|{{BASEPAGENAME}}/Film|Movies}} |
||
| + | {{Tabs2|{{BASEPAGENAME}}/Novels|Novels}} |
||
| + | {{Tabs2|{{BASEPAGENAME}}/Games|Games}} |
||
| + | {{Tabs2|{{BASEPAGENAME}}/Toys|Toys}} |
||
| + | {{Tabs2|{{BASEPAGENAME}}/Books|Books}} |
||
| + | {{Tabs2|{{BASEPAGENAME}}/Comics|Comics}} |
||
| + | {{Tabs2|{{BASEPAGENAME}}/Theme Parks|Theme Parks}} |
||
| + | }} |
||
| + | {{Spoiler}} |
||
| + | ''This article refers to Tyrannosaurus in the [[Jurassic Park franchise#Films|Jurassic Park film canon]]. You may be looking for the [[Tyrannosaurus rex/Novels|novel canon]].'' |
||
| + | |||
{{Dinosaur |
{{Dinosaur |
||
| − | | |
+ | |name = [[File:Rexsequlname.png]] |
| + | |image = Jurassic Park Tyrannosaurus Rex.png |
||
| − | |meaning = Tyrant Lizard King |
||
| + | |caption = Jurassic World Fallen Kingdom Render |
||
| + | |meaning = Tyrant lizard King |
||
|code = ''T. rex'' |
|code = ''T. rex'' |
||
|diet = Carnivore |
|diet = Carnivore |
||
| + | |length = 13.5 meters (44.3 feet) |
||
| − | |length = 13 meters (43 feet)<ref>Henderson DM (January 1, 1999). "Estimating the masses and centers of mass of extinct animals by 3-D mathematical slicing". Paleobiology 25 (1): 88–106.</ref> |
||
| − | |height = 5 meters ( |
+ | |height = 5.5 meters (18 feet) |
| + | |weight = 7 tons (14,000 lbs)<ref name="guide" /> |
||
| − | |weight = 7 tons<ref>Erickson, Gregory M., GM; Makovicky, Peter J.; Currie, Philip J.; Norell, Mark A.; Yerby, Scott A.; & Brochu, Christopher A. (2004). "Gigantism and comparative life-history parameters of tyrannosaurid dinosaurs". Nature 430 (7001): 772–775. DOI:10.1038/nature02699. PMID 15306807.</ref> |
||
| − | |location = USA (Colorado, Montana, Wyoming, Texas, Utah), Canada (Alberta, Saskatchewan) |
||
| − | |range = [[Isla Nublar]]<br />[[Isla Sorna]] |
||
|birth type = Egg |
|birth type = Egg |
||
| + | |range = [[Isla Nublar (movie canon)|Isla Nublar]]<br />[[Isla Sorna (movie canon)|Isla Sorna]]<br/>[[Mantah Corp Island]]<br />[[California]]<br />[[Biosyn Valley]] |
||
| − | |novel = [[Jurassic Park (novel)|Jurassic Park]]<br />[[The Lost World (novel)|The Lost World]] |
||
| + | |film = {{Film|1}}<br>{{Film|2}}<br>{{Film|3}}<br>{{Film|4}}<br>{{Film|5}}<br>''[[Jurassic World: Camp Cretaceous]]''<br>{{Film|6}}<br>''[[Jurassic World: Dominion: The Prologue]]''<br>''[[Jurassic World Camp Cretaceous: Hidden Adventure]]'' (Determinant)<br>''[[Jurassic World: Chaos Theory]]'' |
||
| − | |film = {{film|1}}<br />{{film|2}}<br />{{film|3}}<br />{{film|4}} |
||
| + | |novel = [[Tyrannosaurus rex/Novels|See here]] |
||
| − | |game = ''[[Jurassic Park: The Game]]''<br />''[[Jurassic Park: Operation Genesis]]''<br />''[[Jurassic Park III: Park Builder]]''<br />[[Jurassic Park: Builder]]<br />''[[Jurassic Park: Trespasser]]''<br />''[[Jurassic Park: Survival]]''<br />''[[Jurassic Park: Dinosaur Battles]]'' |
||
| + | |game = [[Tyrannosaurus rex/Games|See here]] |
||
| − | |toy = All |
||
| + | |toy = [[Tyrannosaurus rex/Toys|See here]] |
||
| − | |theme park = }} |
||
| + | |comic = [[Tyrannosaurus rex/Comics|See here]] |
||
| − | {{Quote|The most ferocious and insatiable carnivore ever to step on the face of the planet.|[[Ed Regis]]|Jurassic Park (novel)}} |
||
| + | |book = [[Tyrannosaurus rex/Books|See here]] |
||
| − | {{Quote|We have a T. rex.|[[John Hammond]]|Jurassic Park (movie)}} |
||
| + | |time=Late Cretaceous (72.7-66 MYA)|location=North America<br>Isla Nublar<br>Isla Sorna<br>Biosyn Sanctuary}} |
||
| − | '''''Tyrannosaurus rex''''' (tye-RAN-oh-SAWR-us-recks) is one of the most well-known of all dinosaurs. It is no longer considered the largest of the theropods. ''Tyrannosaurus'' was the last and largest of the {{w|Tyrannosauroidea|Tyrannosaur family}}, or tyrant dinosaurs.<ref name="guide">Holtz T.R., Brett-Surman M., [[Dinosaur Field Guide]], page 128.</ref> |
||
| + | {{Quote|Somewhere on [[Isla Sorna (Movie canon)|this island]] is the greatest predator that ever lived.|[[Roland Tembo]]|The Lost World: Jurassic Park (film)}} |
||
| − | Like other tyrannosaurids, ''Tyrannosaurus'' had very short arms with only two fingers. Although these were probably nearly useless while hunting, its jaws were not: ''Tyrannosaurus'' has an enormous skull armed with teeth the size of bananas. Unlike the teeth of most theropods, the teeth of tyrannosaurids are very thick and capable of crushing bones. The skull and neck bones show that ''T. rex'' had the largest neck muscles of any meat-eating dinosaur. It probably used its strong neck to twist and pull off big chunks of meat that it grasped with its jaws. ''Tyrannosaurus'' could bite with extremely strong force - one fossilized skeleton shows that it crushed and swallowed the bones of a smaller plant-eating dinosaur.<ref name="guide" /> |
||
| + | '''''[[Tyrannosaurus rex]]''''', commonly known as '''''T. rex''''', is a species of theropod dinosaur that lived during the Late [[Cretaceous]] Period, 72 to 66 million years ago. Arguably the most famous species of dinosaur, ''T. rex'' lived in what is now North America, alongside species such as ''[[Ankylosaurus]]'', ''[[Edmontosaurus]]'', ''[[Pachycephalosaurus]]'', ''[[Alamosaurus]]'', ''[[Nanotyrannus]]'', ''[[Triceratops]]'', and ''[[Torosaurus]]''. ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex was among many dinosaur species cloned by [[InGen]] and settled on the [[Costa Rica]]n islands of [[Isla Sorna (movie canon)|Isla Sorna]] and [[Isla Nublar (movie canon)|Isla Nublar]], for use as an attraction for [[Jurassic Park (movie park)|Jurassic Park]], and later, [[Jurassic World (park)|Jurassic World]]. |
||
| − | {{Wikipediainfo}} |
||
| + | An apex predator capable of reaching thirteen meters in length, ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex was the largest species of {{w|Tyrannosauroidea|Tyrannosaurid}}, and was intended to be the star attraction of [[John Hammond]]'s vision for the original Jurassic Park.<ref name="guide">Holtz T.R., Brett-Surman M., [[Jurassic World Dinosaur Field Guide]], page 126-127.</ref><ref name="JP"/> During the [[Isla Nublar Incident (1993)|Isla Nublar Incident]] in 1993, [[Rexy (movie canon)|a female ''T. rex'']] escaped from her enclosure, and became wild on the island.<ref name="JP"/><ref>''[[Jurassic Park: The Game]]'': "[[T. rex Chase]]"</ref> Seven ''Tyrannosaurs'' existed on Isla Sorna, an island in the [[Muertes Archipelago]] originally used by InGen as a cloning facility for their dinosaurs. A family unit consisting of an [[Tyrannosaur Buck|adult male]], an [[Tyrannosaur Doe|adult female]] and an [[Junior|infant]] were encountered during the [[Isla Sorna Incident (films)|Isla Sorna Incident]] in 1997, during which the male was captured and brought to [[San Diego, California|San Diego]], where it was intended to be used in the failed [[Jurassic Park: San Diego|park]], that Hammond had originally envisioned before acquiring Isla Nublar. The animal promptly escaped and [[San Diego Incident| wreaked havoc]] on the city, before being returned to Site B.<ref name="TLW">{{film|2}}</ref> Three years later, another [[Tyrannosaur Bull|male ''Tyrannosaur'']] was [[Rescue of Eric Kirby|encountered]] on Isla Sorna, where it fought and was killed by a ''[[Spinosaurus]]''.<ref name="JPIII">{{film|3}}</ref> Sometime in 2016, [[Big Eatie|two]] [[Little Eatie|female]] ''Tyrannosaurus rexes'' were involved in an incident with the kids of [[Jurassic World: Camp Cretaceous|Camp Cretaceous]] on an [[Mantah Corp Island|island]] owned and operated by [[Mantah Corp]]. |
||
| − | [[File:563140_520393054672249_190382818_n.png|thumb|250px|[[Jurassic Park 3D]] information]] |
||
| − | __TOC__ |
||
| + | The individual from the original park was eventually captured in 2002 and placed in captivity in Jurassic World on Nublar, residing in [[T. rex Kingdom]]. During the climactic events of the 2015 [[Jurassic World Incident]], it was released from captivity and fought and helped defeat, the genetically modified hybrid ''[[Indominus rex]]''.<ref name="JW">{{film|4}}</ref> This same ''T. rex'' became wild once more, though became threatened three years later during the [[Eruption of Mt. Sibo|volcanic eruption]] of [[Mount Sibo]].<ref name="JWFK">{{film|5}}</ref> Before Mount Sibo erupted, many dinosaurs were brought off the island, including the ''T. rex,'' to be [[Lockwood Manor Auction|auctioned off]] at the [[Lockwood Manor]]. The ''T. rex'', along with many other dinosaurs, ended up being [[Dinosaur Outbreak|released into the wild]]. |
||
| − | == Spelling == |
||
| − | ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' is the only dinosaur of which the {{w|Species}} name is well known. For example, most people don't say ''[[Triceratops|Triceratops horridus]] ''or ''[[Stegosaurus|Stegosaurus armatus]]''. However, most people don't know the spelling rules for scientific species names. This has caused ''Tyrannosaurus'' to be the most misspelled dinosaur name. |
||
| − | [[Michael Crichton]] called the creature ''Tyrannosaurus Rex'', or for short ''T-Rex'', in his novels. In most Jurassic Park media and film subtitles the creature is called '''T-Rex''' or '''T. Rex'''. |
||
| + | {{Wikipediainfo|Tyrannosaurus}} |
||
| − | However popular, this spelling is wrong. Dinosaur names are created according to the rules of the {{w|Binomial nomenclature}}. Binomial names consist of two parts. |
||
| − | ''Tyrannosaurus'' is the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genus genus] name, while ''rex'' is the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Species species] name. Genus names must be written with a capital letter but the species name don't. In many cases the (mostly long names) are shortened. In that case, only the first letter of the Genus name is written. That letter is followed by a period, not a "-". All binomial nomenclatural taxon should be written in italics. |
||
| − | Therefore, the taxa be written like this: |
||
| − | * ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' |
||
| − | or for short: |
||
| − | * ''T. rex'' |
||
| + | ==History== |
||
| − | The [[InGen Field Guide]] is one of the few pieces of Jurassic Park media that uses the right names. Although '''T-Rex''' is the most widely used spelling, ''Park Pedia'' shouldn't foster scientific illiteracy. |
||
| + | ===In the Past=== |
||
| + | A later flashback in the Cretaceous showed that a feathered ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex appeared in prehistoric times where it was clashed against a ''[[Giganotosaurus]]'', but it was killed after the battle. A mosquito lands on and bites the dinosaur's right side of the snout, giving the future scientists of [[Jurassic Park (movie park)|Jurassic Park]] the chance to create Rexy, the modern descendant of this very same ''T. rex''. |
||
| + | ===Isla Nublar Incident & Aftermath (1993)=== |
||
| − | ==Portrayal== |
||
| + | {{quote|We have a T. rex!|[[John Hammond]], to [[Ellie Sattler]] and [[Alan Grant]].|Jurassic Park (film)}} |
||
| + | Seven ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' were cloned by [[InGen]] scientists in their [[InGen Compound|compound]] on [[Isla Sorna (Movie canon)|Isla Sorna]], circa 1990.<ref name="TLW" /><ref name="JPIII" /><ref name="JurassicWorld.com">The ''Tyrannosaurus'', according to [[JurassicWorld.com]], had lived on Isla Nublar for 25 years, so ''Tyrannosaurus'' was probably recreated around 1990 or before. This also means that it would have been 3 years old of age at the time of the Isla Nublar Incident of 1993.</ref> [[Rexy (movie canon)|A female ''Tyrannosaurus rex'']] was transported to [[Isla Nublar (Movie canon)|Isla Nublar]] to star as the main attraction of Jurassic Park, inhabiting the [[Tyrannosaur Paddock]].<ref name="JP" /> The paddock was originally intended to be inhabited by an adult, and a juvenile Rex, though it is unknown if a juvenile was ever transported there.<ref>[[File:Trexpaddockoldjw.png|50px]]</ref> |
||
| + | A ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex skeleton was also on display in Jurassic Park's [[Visitor Center]] along with the skeleton of an ''[[Alamosaurus]]''. |
||
| − | ''Note: This article deals with the creature seen in the Jurassic Park franchise, and may have some information that doesn't correspond to what information is available on the actual dinosaur.'' |
||
| + | [[File:Trexfreedomjp1.jpg|thumb|300px|The ''Tyrannosaurus'' breaks out of its paddock during the Isla Nublar Incident.]] |
||
| + | Nublar's ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex was supposed to have been seen by InGen's endorsement team on their [[Park Tour|tour]] of Jurassic Park. However, despite attempts by [[John Arnold|Ray Arnold]] to lure her out of her paddock with [[The Goat (Jurassic Park)|a live goat]], it did not originally reveal herself to the visitors.<ref name="JP" /> When [[Dennis Nedry]] disabled most of Jurassic Park's security with a sophisticated [[Whte rbt.obj|virus]], it was one of the dinosaurs that were able to roam the island freely. One of the embryos Nedry stole from the [[Cold Storage Room]] was ''Tyrannosaurus rex''.<ref name="JP" /> Upon eating the goat that was left for her, the ''Tyrannosaur'' escaped her exhibit and attacked the endorsement team, who were stranded near her paddock, eating [[Donald Gennaro]]. After pushing the [[Explorer 04|tour vehicle]] of [[Lex Murphy|Lex]] and [[Tim Murphy]] off a cliff with Tim inside the vehicle, she attacked Dr. [[Ellie Sattler]] and [[Robert Muldoon]] who were searching for the survivors. After a short chase, she gave up, though.<ref name="JP" /> |
||
| + | The next day, during Grant’s, Tim’s, and Lex’s continued trek to the Visitor Center, they found themselves in the [[Gallimimus Enclosure]], and witnessed a stampeding herd of ''[[Gallimimus]]''. They ran alongside the dinosaurs momentarily before hiding behind a fallen log. The ''T. rex'' suddenly crashed through the nearby bushes next to the stampede stumbling a ''Gallimimus''. This ''Gallimimus'' tried to run away, but was too slow to react, and the ''Tyrannosaur'' lunged at it, catching the dinosaur in her jaws before proceeding to shake the Gallimimus to death. Dr. Grant, Lex, and Tim watched in amazement as the ''T. rex'' started to feast on the carcass. Lex begged Dr. Grant for them to go, to which Grant obliged. However, Tim continued to stare in fascination and so had to be forcibly taken away by Dr. Grant.<ref name="JP"/> She never fully consumed this ''Gallimimus'' and its remains were still present in the location where it had died by October 6, 2002, over a decade later. Her roar was later heard from afar when Dr. Grant and the kids were trying to get through the deactivated electric fence, prompting them to climb over.<ref>[[File:Timack.jpg|50px]] Image from the [[Masrani backdoor]]</ref> |
||
| − | ===Description and Statistics=== |
||
| + | The ''T. rex'' was seen later that day when she had come through the hole in the wall and grabbed a [[Velociraptor (movie canon)|''Raptor'']] from mid-air just as it was to pounce on the humans and crushed it in her jaws. Using the distraction that she provided, the humans fled. Meanwhile, [[The Big One|another ''Raptor'']] that pursued the group through the Visitors Center pounced on the larger theropod. She snapped at her but could not reach her as the raptor continued to rip and tear madly. Rolling her head, the Raptor fell into the ''T. rex's'' mouth where she was killed and then thrown against the ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' skeleton and the T. rex let out a mighty bellow in triumph as the "When Dinosaurs Ruled the Earth" sign fell to the ground.<ref name="JP"/> |
||
| − | ''[[File:Jurassic-park1.jpg|thumb|Rexy next to stacked Ford Explorer reveal her true size. ]]Tyrannosaurus rex'' is described as being capable of running as fast as 32 mph by [[John Hammond]]. |
||
| + | In the aftermath of the incident, the ''T. rex'' went wild and lived on Isla Nublar for about a decade,<ref name="JurassicWorld.com"/><ref name="State"/> probably surviving off any of the herbivorous dinosaurs that managed to survive the incident. |
||
| − | As far as size goes, of the five ''Tyrannosaurs'' to prominently appear in the series, the adult female seen in the first film was 43 feet long and between 16 and 17 feet tall, making her one of largest predators to appear in the Jurassic Park trilogy. The sub-adult male to appear in the third film was listed at 37 feet long and only about 10 feet tall at the hip (inaccurately measured at 14.5ft at the top of the skull, which is not a standard form measurement). The infant to appear in the second film appeared to be no more than 3 feet tall and just 6 feet long. |
||
| + | ===San Diego Incident (1997)=== |
||
| − | They display some sexual dimorphism. Males have more prominent lacrimal ridges than females. Males also have a tendency to have visible facial scaring (possibly due to battles over territory with other ''T. rex'' and carnivores or mates). Females are also brown in color than males, and somewhat larger. Males are slightly smaller than females, and are a molted green in color. They also have a large throat pouch that females seem to lack. Males are typically green ( male T. rexes in ''The Lost world: Jurassic Park'' and the sub-adult male in ''Jurassic Park III''), while females are typically molted brown, (female ''T. re''x in ''Jurassic Park'', female ''T. rex'' in The Lost World.) In Jurassic World the coloration within males also reveals that adults can be a lighter green, have less prominent markings and have yellow markings around their head region, however this is ever seen in most Rexes. |
||
| + | {{quote|I'm trying to change 100 years of entrenched dogma. Dinosaurs were characterized very early on as vicious lizards. There's a great deal of resistance to the idea of them as nurturing parents. Robert Burke said that the T. rex was a rogue, who would abandon its young at the earliest opportunity... I know can prove otherwise.|Dr. [[Sarah Harding]], to [[Ian Malcolm]] during the [[Isla Sorna Incident (films)|Isla Sorna Incident]]|The Lost World: Jurassic Park}} |
||
| + | The ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' on Isla Sorna became wild after [[Hurricane Clarissa]] struck the island, soon after the abandonment of Isla Nublar. They were freed by the workers on the island before they fled. As with the ''T. rex'' on Nublar, to counter the [[Lysine contingency]], ''T. rex'' and the other carnivorous dinosaurs ate herbivores who in turn ate lysine-rich plants as one of their sources of lysine.<ref name="TLW" /> ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' had varying levels of success on Isla Sorna. |
||
| + | [[File:JPTLWBothRexesEddie.jpg|thumb|300px|The male and female ''Tyrannosaurs'' moments before killing [[Eddie Carr]].]] |
||
| + | A ''Tyrannosaur'' family was involved in both the [[Lost World Incident|Isla Sorna Incident of 1997]] and the following [[San Diego Incident]]. Their involvement began when the [[Infant T. rex|son]] was taken from the parents by [[InGen Hunters]] [[Roland Tembo]] and his hunting partner [[Ajay Sidhu]], who intended to use the infant as bait to lure the father, whom Tembo, a seasoned hunter, aspired to kill.<ref name="TLW" /> While the infant called for his parents to rescue, [[Peter Ludlow]] accidentally broke his leg while drunk, when he was startled by the sound of an animal moving through the undergrowth.<ref>{{film|2}} [[The Lost World: Jurassic Park Deleted Scenes#Ludlow Injures the Baby|Deleted Scene]]</ref> |
||
| + | After the [[Gatherers]] freed the dinosaurs captured by the InGen Hunters, [[Nick Van Owen]] discovered the infant ''T. rex''. He decided to take him back to his team's [[Fleetwood RV Mobile Lab|mobile laboratory]], where he and Dr. [[Sarah Harding]] mended the juvenile's leg. However, his parents arrived after first aid was applied, and began to corner the laboratory. Dr. Harding realized that the two ''Tyrannosaurs'' weren't exhibiting hunting behavior so she convinced her fellow Gatherers to hand the young ''T. rex'' to his parents.<ref name="TLW" /> Upon returning the infant to safety, the adult ''Tyrannosaurs ''returned to the mobile lab and began to push it over a cliff. However, [[Eddie Carr]] saved his fellow Gatherers from falling with the RV, but was promptly killed by the predators. Attracted by the smell of blood on Dr. Harding's shirt, the ''Tyrannosaurs'' parents traveled to the new camp of the Gatherers and the Hunters, and attacked the camp.<ref name="TLW" /> |
||
| − | ===Eyesight Debate=== |
||
| − | [[File: |
+ | [[File:JPTLWRexRoarSanDiego.png|thumb|300px|left|The Buck, moments after being freed in San Diego.]] |
| + | While the Hunters fled, the female ''Tyrannosaur'' followed, killing many of them in the process. As the ''Tyrannosaur'' Buck continued his search, he was tranquilized by Roland Tembo (due to the fact that Nick Van Owen stole the bullets intended to hunt the dinosaur). After the female ''Tyrannosaur's'' attack, Peter Ludlow ordered the remaining InGen Hunters to secure the ''Tyrannosaur'' Buck and recapture the juvenile ''T. rex'' for [[Jurassic Park: San Diego]]. But his plan went astray when the ''Tyrannosaur'' Buck escaped confinement upon reaching [[San Diego, California]] and went rampaging throughout the city, killing several civilians.<ref name="TLW" /> |
||
| − | Dr. [[Alan Grant]] states that the sight of ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' is based on movement, so if you don't move the animal won't see you. Alan Grant uses this knowledge to escape from the ''T. rex'' in the novel, and the first and third movies. |
||
| + | To stop the chaos, gatherers Sarah Harding and [[Ian Malcolm]] broke into [[Jurassic Park: San Diego]] to steal the baby ''Tyrannosaur'' so they use him to lure his father back into [[InGen Waterfront Complex|the docks]]. The plan worked, but when Peter Ludlow tried to recapture the juvenile, he was crippled by the ''Tyrannosaur'' Buck and finished off by the infant. The ''Tyrannosaur'' Buck's rampage ended when Dr. Harding tranquilized him before the San Diego police could shoot him. Both ''Tyrannosaurus'' father and son were reunited once more with the female when they were transported back to Isla Sorna.<ref name="TLW" /> |
||
| − | But, as stated (in the second novel) by Dr. [[Richard Levine]], this is very unlikely because many animals (including humans) freeze or play dead when they are scared. If the ''Tyrannosaurus'' wasn't able to see non-moving creatures, it would miss most of its prey. Richard Levine explains the previous instances in which people escaped from the ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' by freezing with: "the only reason it would not eat you is if it was not hungry." |
||
| + | As a result of the San Diego Incident, Isla Sorna, and presumably Isla Nublar, were designated as restricted areas. In 1999 [[Henry Wu|Dr. Wu]] secretly returned to Site B, and illegaly cloned several new dinosaurs. One of which was a ''Spinosaurus'' that managed to claim the north side of Isla Sorna as its territory. |
||
| − | Supporting Dr. [[Alan Grant]]'s theory is that the ''Tyrannosaurus'' may not be able to see you, so to counteract this, the ''T. rex'' gives a loud roar to scare its prey into revealing their position by running away. The ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' may then make the kill. Supporting Levine's theory, in [[Jurassic Park (novel)|Jurassic Park]] the T.rex, when it escapes from its paddock, eats [[Donald Gennaro]] which may have satisfied its hunger. This may be why, instead of the ''Tyrannosaurus'' eating Grant as well, it only gave a roar to scare him out of her territory. This way the threat to her territory was eliminated. |
||
| + | ===Rescue of Eric Kirby (2001)=== |
||
| − | In the second novel, [[Michael Crichton]] takes the blame of the wrong theory, that ''Tyrannosaurus'' sight is based on movement, away from Dr. Alan Grant. It is stated that the paleontologist Dr. [[John Roxton]] wrote an article in which he stated that the brain of the ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' was very similar to that of frogs. Therefore, Dr. Roxton concluded that ''T. rex's'' sight was based on movement. Alan Grant and also the biologist [[George Baselton]] had no expertise in brain anatomy and accepted the conclusions of the article. |
||
| + | [[File:Bull rex.jpg|thumb|258x258px|A T. rex was found by Dr. Alan Grant and a group of people during a rescue mission to Isla Sorna in 2001.]] |
||
| + | In 2001, [[Eric Kirby]], a teenage boy marooned on the island from illegal sight-seeing, collected ''T. rex'' urine that he used to deter small carnivorous dinosaurs such as ''[[Compsognathus]]'' though he also learned that it attracted the island's intensely territorial ''Spinosaurus''.<ref name="JPIII" /> Weeks later, a [[Tyrannosaur Bull|male ''T. rex'']] encountered a group of people led by Dr. [[Alan Grant]], who travelled to Isla Sorna to rescue Kirby, while eating a ''[[Parasaurolophus]]''.<ref>CG Supervisor of ''Jurassic Park III'' [[Christophe Hery]] identifies the carcass as ''Parasaurolophus''. Furthermore, the prop used is the carcass from ''The Lost World: Jurassic Park'' repainted.</ref><ref name="JPIII" /> |
||
| + | [[File:Rexvsspino01.jpg|thumb|258x258px|The male ''T. rex'' faces off against the ''Spinosaurus''.|left]] |
||
| + | Grant tried to avoid the ''T. rex'' by standing still, but the ''Tyrannosaur'' noticed them and gave chase, bringing him into contact with [[Asset 87|the ''Spinosaurus'']]. The two theropods sized each other up and began to [[Spinosaurus vs. T. rex Scene|fight]]. The ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex was the first to attack in the dual, biting down on the neck of the ''Spinosaurus'' and bringing it down to the forest floor. The ''Spinosaurus'' regained balance, however, and began to snap at his flanks. After the ''Spinosaurus'' swiped at him, the ''T. rex'' rammed his opponent head first, resulting in the ''Spinosaurus'' biting down on the ''T. rex's'' neck. As the Rex roared in agony, the ''Spinosaurus'', with support from its arms, proceeded to snap its neck. The ''T. rex's'' body collapsed to the ground, nearly crushing Dr. Grant while escaping. The ''Spinosaurus'' then claimed the carcass of its fallen foe triumphantly.<ref name="JPIII" /> |
||
| + | ===[[The Evolution of Claire]] (2004)=== |
||
| − | It is possible that since it was a predator with binocular vision, ''Tyrannosaurus'' had trouble seeing stationary prey in the dark, though this is a dubious theory. Dr.Grant suggested should be applied (the 'don't move' tactic) on Isla Sorna when they stumbled upon a ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' - in broad daylight. The ''T. rex'' killed Gennaro because he while he was still in one place, he was visibly shaking and moving his arms, therefore revealing his position to the ''T. rex''. Some parts of Gennaro were found when Malcolm was discovered. In [[Jurassic Park III]], the characters in the story run into a ''Tyrannosaurus'' devouring its prey (''[[Parasaurolophus]]'' according to the special effects commentary). The ''T. rex'' then gives a roar scaring the party into running away. The ''Tyrannosaurus'' then chases the group. This ironically can support either side of the debate. The ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' may have not been able to see the group so it scared them into running so he could find them or he may have not been hungry from eating its prey, so it just wanted to scare the group away by roaring and chasing them away. Supporting this is the fact that in the [[Jurassic Park (novel)|Jurassic Park novel]] and [[Jurassic Park (film)|film]], the ''Tyrannosaurus ''chases a jeep away from her territory then ceases the pursuit despite the fact that she could have easily destroyed the jeep. |
||
| + | {{quote|Well, if there is a queen of dinosaurs, it's probably her.|[[Bertie]], describing the ''T. rex'' to Claire|The Evolution of Claire}} |
||
| − | {{-}} |
||
| + | The original ''T. rex'' from [[Jurassic Park (movie park)|Jurassic Park]], dubbed "Rexy," was contained in a paddock near [[Main Street]] for [[Jurassic World (park)|Jurassic World]]. Her paddock was described as being densely packed with jungle growth, with a viewing booth on a transparent wall that overlooked the enclosure. She was normally fed live meat, typically goats as that was her preference, but once a month she was given meat mixed with amino acids and other nutrients to keep her healthy and strong; a flare was used for visual aid since she associated it with food. Her behavior was often withdrawn, which would be mistaken as shyness, but it was explained that she "decided [humans] need to earn her respect." She was considered wise, calculating, and curious. |
||
| + | ===Jurassic World (2005-2015)=== |
||
| − | ===Hunting=== |
||
| + | {{quote|We need more teeth!|[[Gray Mitchell]], inspiring [[Claire Dearing]] to release the ''T. rex'' on the ''Indominus''|Jurassic World (film)}} |
||
| − | [[File:Tyrannosaurus Rex Escapes.jpg|250px|thumb|The ''Tyrannosaurus'' escapes]] |
||
| + | On April 19, 2002, during the planning stages for the construction of a new park on Isla Nublar known as [[Jurassic World (park)|Jurassic World]], Rexy was captured by an [[InGen Security Division|InGen security team]] led by [[Vic Hoskins]].<ref>In the archived message "[[Masrani backdoor#WEEK 3|WEEK 3]]" of the [[Masrani backdoor]] Vic Hoskins writes about "staring a seven-ton predator in the eyes" in the first year of construction of Jurassic World, in which InGen Security was on Isla Nublar to defend the construction workers there. The only predator known on Isla Nublar that reaches this weight is ''Tyrannosaurus'' and since there was no other ''T. rex'' confirmed to have been on the island at the time of the 1993 Isla Nublar Incident, the creature encountered by Hoskins was the ''T. Rex'' on Isla Nublar.</ref> The ''Tyrannosaur'' was placed in the [[T. rex Kingdom]] attraction, where she was intended to serve as one of Jurassic World's most popular animals once the park was open in 2005.<ref name="Rexy">The article for the [[T. rex Kingdom]] on [[JurassicWorld.com]] says that the ''Tyrannosaurus'' that resides there has lived on Isla Nublar for twenty-five years. This is the only ''T. rex'' confirmed to have lived on Isla Nublar, so this individual is the same as her. This is further confirmed in a [http://www.slashfilm.com/jurassic-world-performance-capture/ SlashFilm] article discussing {{film|4}}'s performance capture and an interview with director [[Colin Trevorrow]].</ref> Though she was the only T. rex known to live in the park, there was a Cold Storage room for ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex present in the [[Hammond Creation Lab]] in the mid-2010s.<ref>[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pYFdE_E3mSM Jurassic World - Inside the Hammond Creation Lab (HD)]</ref> |
||
| − | ''Tyrannosaurus'' were depicted as apex predators and as such spent a lot of time following game trails. They seemed to prefer to ambush prey animals, and it was once thought that this was possibly because of their motion sensitive eyesight, which has since been disproved. It was once theorized that most prey animals freeze when afraid because the ''Tyrannosaurus'' supposedly lacked the ability to see [[File:Tyrannosaurus-eating-goat.jpg|thumb|left|250px|A ''Tyrannosaurus'' eating a goat. ''([[Jurassic Park]])'']]stationary prey. In actuality, ''Tyrannosaurus'' have an excellent binocular vision. (''see'' [[Tyrannosaurus rex#Eyesight Debate|Eyesight Debate]]) The ''Tyrannosaurus'' are not random killers, however, and are less likely to attack when full. |
||
| + | [[File:Rexy_preparing_for_battle_with_Indominus_rex.jpg|thumb|left|300px|Rexy smashes through the ''[[Spinosaurus]]'' skeleton prior to her fight with the ''[[Indominus rex]]''.]] |
||
| − | {{-}} |
||
| + | The base genome of the ''[[Indominus rex]]'', a genetically engineered hybrid that caused the [[Isla Nublar Incident (2015)|second incident]] on Isla Nublar was ''Tyrannosaur''.<ref name="JW" /> During the hybrid's rampage across the island, Rexy remained in her enclosure. |
||
| + | The wreck of the ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' skeleton remained in the ruins of Jurassic Park's visitor center since the incident 12 years ago. [[Zach Mitchell]] used a rib from the skeleton along with a piece of the "When Dinosaurs Ruled the Earth" banner to make a torch when he and his brother [[Gray Mitchell|Gray]] explored the place. The skull was later crushed under the weight of the ''Indominus rex's'' hand when it chased [[Owen Grady]] and [[Claire Dearing]] in the same area before being pursued by the [[JW001]]. |
||
| − | === Parenting === |
||
| − | In ''[[The Lost World (novel)|The Lost World]]'' novel and [[The Lost World:Jurassic Park (film)|the film adaptation]], ''Tyrannosaurus'' is shown as being a protective parent. ''Tyrannosaurus'' are shown to pair off during mating, and both parents will remain with their offspring during its growth, exhibiting very powerful parenting and protective instincts, going to great lengths to ensure an infant's safety. ''Tyrannosaurus'' are territorial by nature, and will attempt to drive away anything that might be deemed dangerous, whether animate or not. They are known to be efficient parents, with both male and female keeping close guard over infants and bringing them food for a considerable matter of months. They will ferociously defend their offspring during this stage from predators and humans, and will even travel far outside their native territories to find them if they get lost. Like most predators, they presumably teach their young how to hunt once the time comes. |
||
| + | Rexy was eventually released by [[Lowery Cruthers]] under the orders of Claire, who lured it to fight against the ''Indominus''. Smashing through the skeleton of a ''Spinosaurus'', it roared threateningly at the ''Indominus'', and the two began a vicious [[Battle of Main Street scene|fight]]. |
||
| − | While no T. rex nest has yet been found in the real world, the living relatives of ''Tyrannosaurus'' (birds and crocodilians) guard their nests and take care of their babies. Similarly, there is evidence from nests of smaller meat-eaters and from various plant-eaters that many dinosaurs were good parents. So the simplest explanation at present is that, fearsome though it may have been, ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' probably looked after its eggs and young.<ref name="guide" /> |
||
| + | The two predators seemed evenly matched, however, the ''Indominus'' overpowered Rexy with her strong forearms. Just when the ''Indominus'' was about to finish her off, the ''Velociraptor'' [[Blue]] attacked the hybrid, allowing the veteran ''Tyrannosaur'' to overpower the ''Indominus'', pushing it to the side of the [[Jurassic World Lagoon]], where the park's ''[[Mosasaurus]]'' leaped from the water, and dragged the hybrid into the depths. Briefly looking at Blue, Rexy turned away and slowly made her way into the jungle.<ref name="JW" /> Free on the island once more, she made her way to the top of the Jurassic World's control center, and roared triumphantly.<ref name="JW" /> |
||
| − | [[File:T.Rex.jpg|thumb|T.Rex fanart by Hellraptor]] |
||
| − | ==[[Jurassic |
+ | ===''[[Jurassic World: Camp Cretaceous]]'' (2016)=== |
| + | A mother-daughter pair was taken from Isla Sorna and placed in the jungle biome on the island [[Mantah Corp]] owned. The mother was nicknamed "[[Big Eatie]]" and the daughter was nicknamed "[[Little Eatie]]." They were at one point forced into fighting each other due to a BRAD tainting their food, and later Big Eatie was forced to fight a ''[[Kentrosaurus]]'' named [[Pierce]]. |
||
| − | ''Tyrannosaurus ''is one of the most popular dinosaurs in the Jurassic Park franchise. It appeared as the main super-predators in the novels and first two films, it appears in [[Jurassic Park III]] but only in one scene fighting the ''[[Spinosaurus]]''. It appears in every video game, mostly as a boss. ''Tyrannosaurus'' is also featured in all the toy lines as well. |
||
| + | ===Eruption of Mount Sibo (2018)=== |
||
| − | ==Novels== |
||
| + | {{Quote|The T. rex would be dead by now, right?|[[Franklin Webb]].|Jurassic World: Fallen Kingdom}} |
||
| − | ===[[Jurassic Park (novel)|Jurassic Park]]=== |
||
| + | [[File:IMG_20180905_092958.jpg|thumb|300px|Rexy subdues a ''[[Carnotaurus]]'' during the eruption of [[Mount Sibo]].]] |
||
| − | [[File:14989 0950 1 lg.jpg|250px|thumb]] |
||
| + | After the ''Indominus'' rampage throughout Jurassic World, Isla Nublar was once again abandoned to the dinosaurs, left to their own devices without human interference. |
||
| − | In [[Jurassic Park (novel)|Jurassic Park]], InGen recreated the ''Tyrannosaurus''. Two ''Tyrannosaurus'' were present on [[Isla Nublar]]; one adult and one juvenile, although there was no interaction between them. The ''Tyrannosaurus'' had a sensitive skin, and therefore sought shelter from the sun under the canopy. It was stated in the novel that dinosaurs are weak in noticing unmoving objects, although this may not be the case. |
||
| + | A few months after Jurassic World fell, Rexy attacked a group of mercenaries. One man is left on the ground and their helicopter lets down a rope ladder. They escape the ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex but the man on the rope ladder is swallowed by the ''Mosasaurus'' after it jumps into the air, and the ''Mosasaurus'' escapes from its pen into the ocean.<ref name="JWFK">{{Film|5}}</ref> |
||
| − | After the power cut, when the creatures break free of confinement and attack the cars. The adult didn't kill anyone, although it nearly killed Dr. Malcolm and almost ate Tim. The juvenile killed [[Ed Regis]]. The creature was also a surprisingly good swimmer, described as swimming much like a crocodile, though this is very unlikely in real life. |
||
| + | Three years after the abandonment of the park, and two years after she messed with the mercenaries, [[Mount Sibo]], the volcano which provided geothermal power to the original park, began to erupt, prompting Claire Dearing to organize a mission to rescue the dinosaurs from the doomed island.<ref name="JWFK" /> |
||
| − | [[File:JurassicPark-TRexRampage.jpg|thumb|left|250px]] |
||
| + | [[File:Finaltrailer28vo2p.jpg|thumb|left|300px|Rexy sleeping in transport truck.]] |
||
| − | Dr. Grant and the children later find it sleeping as they raft down a river. When Lex coughs uncontrollably it wakes up and takes to the water, swimming after them, but soon abandons the pursuit when the juvenile ''T. rex'' tries to move in on the adult's onshore kill. Muldoon later shoots it with a very large tranquilizer dart, which causes the ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' to pass out while it was trying to eat Tim, saving Dr. Grant and the children who were seeking refuge behind a waterfall. It is possible, although not directly mentioned, that the adult ''Tyrannosaurus'' drowned. The survivors, fleeing by helicopter, have one last look at the juvenile before it and the other dinosaurs are destroyed. |
||
| + | At some point during the mission, in the midst of a stampede away from the eruption, Rexy attacked and fatally subdued a ''[[Carnotaurus]]'', inadvertently saving Owen, Claire, and [[Franklin Webb]].<ref name="JWFK" /> |
||
| − | {{-}} |
||
| + | The ''Tyrannosaurus'' was later captured and, in a desperate attempt to save Blue, Claire and Owen had to get some of her blood. They found the Tyrannosaur and successfully got her blood but were locked in by some guards and Rexy woke up. As the agitated animal began to freak out and thrash violently, Claire escaped through the top and opens the main doors of the cage; Owen narrowly escapes the ''T. rex''’s snapping jaws before she can bite him in half.<ref name="JWFK" /> |
||
| − | ===[[The Lost World (novel)|The Lost World]]=== |
||
| − | In [[The Lost World (novel)|The Lost World]], one pair of ''Tyrannosaurus'' is present at [[Isla Sorna (Novel canon)|Isla Sorna]]. They have a nest on the east side of the island. A team led by Dr. [[Ian Malcolm]] arrive at the island to rescue Dr. [[Richard Levine]]. But when the male ''T. rex'' sees their car in his territory the male puts his flag on the car. The ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' pretends to attack Dr. [[Jack Thorne]] and Dr. [[Richard Levine]] to make them leave their territory. The team of Dr. [[Lewis Dodgson]] tries to steal the eggs of ''Tyrannosaurus'', but the attempt fails and [[George Baselton]] gets eaten. |
||
| + | [[File:The T. rex eating the remains of Eli Mills.jpg|thumb|left|The T. rex eating the remains of Eli Mills with the [[Carnotaurus]]]] |
||
| − | One of ''T. rex'' infants is wounded, therefore [[Eddie Carr]] takes the infant to the trailers and the team puts a temporary cast on its broken leg. But before they can bring the infant back, the parents have reached the trailers to collect their child. Once the child is safe, they attack the trailers and push them over the cliff. |
||
| + | [[File:REXY_BADASS.jpg|thumb|right|300px|''Tyrannosaurus'' roaring after killing Mills.]] |
||
| + | She was put into a cage underneath [[Lockwood Manor]] and, after nearly suffocating from a hydrogen cyanide leak, she was saved by being released by [[Maisie Lockwood]] into America. But before she leaves, Rexy suddenly reappears and snatches [[Eli Mills]] in her jaws, brutally shredding him before tearing him in half with a ''Carnotaurus'', and ultimately devouring Mills, Rexy then knocked over the ''Carnotaurus'' with her head and the ''Carnotaurus'' got up and ran off. Then Rexy roared and walked away, crushing the ''I. rex'' fragment in the process and ensuring that no carnivorous hybrid could ever wreak havoc upon the world again.<ref name="JWFK" /> |
||
| + | After she [[Dinosaur Outbreak|escaped]], Rexy broke into a nearby zoo and roared at a male African lion, who stood his ground by angrily roaring back at her.<ref name="JWFK" /> As the T. rex began to break into the zoo roaring at the male lion, the zoo's staff attempted to capture her. The T. rex bit at the rope carrying the cage by a helicopter before she managed to escape back into the forest. |
||
| − | The ''Tyrannosaurus'' tries to get [[Sarah Harding]] and Dodgson, who are hiding under a car. Dr. Harding pushes Dr. Dodgson away and the ''T. rex'' takes Dr. Dodgson to his nest as food for the infants.[[File:Novel_T.rex.jpg|thumb|Fanart by Hellraptor]] |
||
| + | ===''[[Jurassic World: Dominion]]''=== |
||
| − | ==Movie canon== |
||
| + | Four years later, [[Rexy (movie canon)|Rexy]] unintentionally attacked a drive-in movie theater as she was being chased by the [[Department of Prehistoric Wildlife]]. After three years, she was finally captured and taken to [[Biosyn Research Facility|Biosyn Genetics Santuary]]. |
||
| − | ===''Jurassic Park''=== |
||
| − | [[File:TJP.JPG|right|250px|thumb|The female begins dismantling the car]] |
||
| − | In {{film|1}}, the ''Tyrannosaurus'' was to be one of the main attractions at ''[[Jurassic Park (movie park)|Jurassic Park]]''. The female in this film (nicknamed ''[[Rexy]]'') is supposedly the largest ''Tyrannosaurus'' seen in the series, at 13 meters (43 feet) long and between 5.2-4.9 meters (16-17 feet) tall. This makes her one of the largest ''Tyrannosaurus'' on record. |
||
| + | During her first day in the sanctuary, Rexy attempted to eat a dead deer in the forest before the then-current apex, ''[[Giganotosaurus]]'', interrupted. Their scuffle was short and ended with Rexy backing off, leaving the area and her meal to her opponent. After Lewis Dodgson's flaming ''[[Giant locust|giant locusts]]'' escaped the facility and set the forest on fire, Rexy was commanded to reach safety at the [[Biosyn Research Facility|emergency zone]]. Rexy and the ''Giganotosaurus'' clashed once more, this time with the latter briefly killing the former. After a distraction from [[Kayla Watts]], the ''Giganotosaurus'' fought the nearby ''[[Therizinosaurus]]''. Returning to life, Rexy shoved the ''Giganotosaurus'' into the claws of the ''Therizinosaurus'', impaling and killing it. The two then roared in victory after the fight. Sometime later, Rexy was met by two other tyrannosaurs, the [[Tyrannosaur Buck|Buck]] and [[Tyrannosaur Doe|Doe]], who had also been in the valley prior to her arrival.<ref>Confirmed by Colin Trevorrow that they are Buck and Doe.</ref> |
||
| − | [[John Hammond]] reveals the park has a ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' shortly after the visitors arrive on the island. [[Ellie Sattler|Ellie]] was very shocked to hear about the T. rex. Dr. Grant almost fainted. When the visitors reach the [[Tyrannosaur Paddock]], the ''Tyrannosaurus'' doesn't appear; even when it is lured with a goat. |
||
| + | ==Characteristics== |
||
| − | At night the tour vehicles are stranded right near the T. rex paddock. After being attracted to the waving flashlight in the lead car, she attacked the car and its passengers. It killed [[Donald Gennaro|Gennaro]] and wounded Dr. [[Ian Malcolm|Malcolm]]. After failing to pinpoint Grant and Lex's location, it attempted to flush them out by pushing the wrecked lead car down the road and off a steep incline in its enclosure. |
||
| + | ===Physical attributes=== |
||
| + | ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' cloned by InGen had fully scaled skin as juveniles and as adults,<ref name="TLW" /> when it is considered by scientists that ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex was feathered at least some parts of its body. The presence of feathers was seen in the naturally born individuals seen in the sequence taking place in the Cretaceous Period, where an adult ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex sports a short cape and mane of filamentous feathers across its back, neck, and shoulders. Its skin was thick, being able to offer some resistance to the razor-sharp toe claws of a ''[[Velociraptor (movie canon)|Velociraptor]]'',<ref name="JP"/> and the sharp claws of the hybrid ''[[Indominus rex]]'' that were able to debilitate a full-grown ''[[Apatosaurus]]'' as well as the strong bite of the ''Indominus'', which was able to crack the bulletproof glass of a [[Gyrosphere]].<ref name="JW"/> However, many of the adult Tyrannosaurs encountered by humans would bear at least one scar that would be found on their head or neck. Two adult males had a single scar on the side of their face.<ref name="TLW" /><ref name="JPIII" /> The individual from Isla Nublar had several scars on her neck from a cloned ''Velociraptor'' that pounced on her.<ref name="JW" /> According to evidence from the encounter between a Spinosaurus and a Tyrannosaurus rex on Isla Sorna, it suggests that the neck muscles of Tyrannosaurus rex could potentially be a vulnerable area. The Spinosaurus was able to successfully kill a Tyrannosaurus rex and nearly defeat another individual called "Big Eatie." Additionally, a Gigantosaurus was able to overcome an ancestor of the Tyrannosaurus rex. These instances indicate that the neck muscles of Tyrannosaurus rex may have been a weak spot, susceptible to attacks from certain predators. |
||
| + | [[File:Tyrannosaurus-family.jpg|thumb|300px|left|A ''Tyrannosaur'' family unit on [[Isla Sorna]] in 1997.]] |
||
| + | {{w|Sexual dimorphism}} was present in the recreated ''Tyrannosaurus rex'', such as the males having a throat wattle and much more prominent brows.<ref name="BuckScenes" /> The males also had deeper vocalizations than the females<ref name="TLW" /><ref name="JPIII" />, though the female ''T. rex'' of Isla Nublar also had deepened vocalizations when she got older.<ref name="JW" /> Every adult Tyrannosaur encountered each had their own unique skin color and pattern. Males tended to have a green skin color and females tended to have a brown color while the juvenile known as Junior was a mix of the two aforementioned colors.<ref name="Skin">Comparison between Rexy, ([http://vignette2.wikia.nocookie.net/jurassicpark/images/1/1d/Trexwithstanwisnton.jpg/revision/latest?cb=20160512052001 young] and [http://vignette2.wikia.nocookie.net/jurassicpark/images/f/f8/T-Rex.png/revision/latest?cb=20141128030334 old]) [http://vignette1.wikia.nocookie.net/jurassicpark/images/6/67/Tyrannosaurbuckanimatronic.png/revision/latest?cb=20160512052351 the Buck], [http://vignette3.wikia.nocookie.net/jurassicpark/images/e/ef/Tyrannosaurdoe.png/revision/latest?cb=20160421212757 the Doe], [http://vignette3.wikia.nocookie.net/jurassicpark/images/4/49/Juniorbetter.png/revision/latest?cb=20160708034529 Junior] ([http://vignette3.wikia.nocookie.net/jurassicpark/images/9/99/Tyrannosaurbabybrown.png/revision/latest?cb=20160706203151 additional shot]), and finally, the [http://vignette4.wikia.nocookie.net/jurassicpark/images/6/60/T-Rex_size.png/revision/latest?cb=20140916024049 ''Jurassic Park III'' ''T. rex''].</ref> |
||
| + | According to founder and former CEO of InGen [[John Hammond]], the cloned ''T. rex'' could run at speeds of 32 mph.<ref name="JP">{{film|1}}</ref> The clones seemed to have had an accelerated growth cycle as the ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' of Isla Nublar was the size of a 28-year-old when she was only five<ref name="Rexy" /><ref name="State">''Jurassic World'' director [[Colin Trevorrow]] as well as [[Industrial Light and Magic]] members [[Geoff Campbell]] and [[Steve Jubinville]] have stated that the ''T. rex'' from ''Jurassic World'' was indeed the same individual that appeared in ''Jurassic Park''.</ref> and the only juvenile observed, Junior, was the size of a two-year-old tyrannosaurid yet was still highly dependent on his parents.<ref name="TLW" /> |
||
| − | [[File:Tyrannosaurus Eating.JPG|250px|thumb|left|''T. rex'' kills the Gallimimus.]] |
||
| − | Later, when Ellie and [[Robert Muldoon|Muldoon]] arrived in a jeep searching for Dr. [[Alan Grant|Grant]] and the children, the female returned and promptly charged at their jeep, pursuing it out of the vicinity, then ended the pursuit just as they crashed through a fallen tree. |
||
| + | In 2018, the [[Dinosaur Protection Group]] website uploaded an informative graphic for the "average" InGen ''Tyrannosaurus rex'', with a length of 12 meters (39.4 feet, though this is commonly rounded up to a simple 40 feet in the franchise) and 7 tons (14,000 pounds).<ref>https://jurassicpark.fandom.com/wiki/File:T-rex_dpg.jpg</ref><ref>https://i.imgur.com/ENqkAof.jpg Jack Ewins clarifying the DPG graphic.</ref> However, one female specimen had grown larger, measuring over 13.5 meters (44.3 feet) long and standing over 5.5 meters (18 feet) tall. |
||
| − | The ''T. rex'' appears again in the ''[[Gallimimus flocking scene]]''. As Dr. Grant and the children were making their way through the park, they were nearly trampled by stampeding ''[[Gallimimus]]'', which were running from the ''T. rex''. She came bursting out of the woods and killed one of the Gallis. |
||
| + | [[Rexy (movie canon)|Rexy]], a late 20-year-old ''Tyrannosaurus rex'', exhibited remarkable stamina and endurance as she pursued [[Claire Dearing|Claire]] relentlessly from the confines of her enclosure all the way to [[Main Street]], where she encountered the decorative skeleton of a ''[[Spinosaurus]]''. Despite sustaining injuries, Rexy valiantly engaged in a [[Battle of Main Street scene|brutal confrontation]] with the ferocious ''[[Indominus rex]]''. Surprisingly, her stamina did not falter even in the face of adversity. With the assistance of [[Blue]], another dinosaur (''[[Velociraptor/Film|Velociraptor]]''), Rexy prolonged the fight against the ''Indominus rex'' until its eventual demise on Main Street. Following this arduous battle, Rexy managed to walk away, triumphantly leaving the scene. |
||
| + | ===Behavior=== |
||
| − | [[File:JP-WhenDinosaursRuled.jpg|250px|thumb|right|Inside the Visitors' Center]] |
||
| + | Unlike their prehistoric forebears, ''Tyrannosaurs'' bred by InGen were thought to hunt prey by seeing movement, likely considering stationary objects to be less of a threat.<ref name="JP" /><ref name="TLW" /><ref name="JPIII" /><ref name="JW" /><ref>Cohn, Paulette. (June 12, 2015) [http://www.biography.com/news/jurassic-world-jack-horner-interview Jurassic World's Dinosaur Expert Talks Facts vs. Fiction (INTERVIEW)]. ''Biography''</ref> This theory would be called into question during an incident on Isla Nublar where social media influencer [[Brooklynn]] tricked a ''T. rex'' into attacking a static cardboard cutout bearing her likeness. <ref>[[A Beacon of Hope]]</ref> From what has been observed of wild ''Tyrannosaurs'', they were solitary animals, though a breeding pair on Isla Sorna roamed in the island in a pack.<ref name="JPIII" /> |
||
| − | Her final appearance was as the unlikely heroine in the ''[[T. rex Rescue Scene]]''. In the Visitor Center, the visitors are trapped by [[Velociraptor (movie canon)|raptors]], which are about to attack. Rexy bursts into the Visitor Center and grabs one of the raptors. The other raptor attacks Rexy, but Rexy kills it without much trouble. In this way, the visitors could escape with their lives. |
||
| + | [[File:TLWFemRex.jpg|thumb|300px|Both male and female ''Tyrannosaurs'' were fiercely protective of their infants.]] |
||
| − | {{-}} |
||
| + | Contrary to [[Robert Burke]] beliefs, supports the idea that Tyrannosaurs, including Tyrannosaurus rex, exhibited caring parental behaviors. Dr. Sarah Harding's theory, which aligns with current understanding, suggests that T. rex parents took care of their young. The offspring would remain in a nest while the parents provided food for them for approximately two weeks, until the juveniles were able to hunt independently. |
||
| + | While the exact number of eggs and young in a T. rex litter remains uncertain, it is known that if a T. rex baby went missing, the parents would actively search for it, relying on the cries of the missing offspring or the scent of its blood. However, if the parents were too far away to hear the calls, they likely relied on their territorial boundaries to protect their offspring within their home. |
||
| − | ===''Jurassic Park: The Game''=== |
||
| + | If Tyrannosaur parents detected the scent of their offspring's blood on a potential threat, they would confront and address the perceived danger. This behavior indicates a strong protective instinct and a willingness to defend their young. |
||
| − | [[File:T-Rex in main lobby in Visitor Center JP Telltale.jpg|thumb|250px|Rexy in the Visitor Center]] |
||
| + | The observations of family, like Big Eatie and Little Eatie provide evidence that mother and daughter Tyrannosaurus rex can remain together as a family, even when the daughter reaches a size comparable to her mother or close to it as sub adult. Despite uncertainties about the exact age at which Little Eatie would typically become independent, she still appears to rely on her mother for guidance. The limited environment they inhabit may contribute to the daughter's continued presence with her mother, as it may not provide sufficient resources or suitable conditions for her to venture out on her own. Little Eatie has demonstrated her strength by successfully defending herself against aggressive dinosaurs, but she also exhibits signs of fear when confronted with overwhelming numbers, prompting her mother to intervene and protect her. |
||
| − | [[File:untitled.png|thumb|250px]]The ''Tyrannosaurus'' appeared in Telltale's [[Jurassic Park: The Game]] as one of the main antagonists. The ''T. rex'' is the same one seen in the first film. |
||
| + | In their interaction, Big Eatie and Little Eatie frequently partake in playful displays of aggression, emulating the semblance of a genuine fight. This behavior is characterized by vigorous cranio-facial biting and jovially pushing each other using their bodies. The aforementioned conduct, as witnessed during the interaction between Big Eatie, the maternal figure, and her daughter, is indicative of their spirited and lighthearted approach. |
||
| − | It is first seen in ''[[Triceratops Trouble]]'', where it faces off against [[Lady Margaret]], the alpha ''[[Triceratops]]'', almost killing [[Gerry Harding/Jurassic Park:The Game|Gerry Harding]], his daughter [[Jessica Harding|Jess]], who had come to visit the island earlier, and a very ill [[Nima Cruz]], who was unconscious at the time. The two of them narrowly escape with their lives and wait out the night in the [[Triceratops Maintenance Building]] as the two titans clash. |
||
| + | ''Tyrannosaurs'' reflected a high level of intelligence in several instances. The individual of Isla Nublar, in particular, has shown a good deal of intelligence during both the [[Isla Nublar (Movie canon)|Isla Nublar]] incidents in both [[Isla Nublar Incident (1993)|1993]] and [[Isla Nublar Incident (2015)|2015]]. In the former, she tested the electrical fences after the power outage, seemingly aware of the lack of power before attempting to escape.<ref name="JP" /> During the incident in 2015, it showed enough intelligence not to attack [[Blue]] during and after their fight with the ''Indominus'', aware of the key role the ''Velociraptor'' played in distracting the hybrid as it attempted to kill her.<ref name="JW" /> Both the [[Tyrannosaur Buck|male]] and [[Tyrannosaur Doe|female]] ''Tyrannosaurus'' during the [[Lost World Incident|Isla Sorna Incident]] in 1997 also showed a high degree of intelligence, seen in their efforts to protect their [[Junior|infant]] from the humans, even going so far as to push a trailer over a cliff and hunt in a familial pack.<ref name="TLW" />[[File:RexyMeetsBuckandDoe.PNG|thumb|[[Rexy (movie canon)|Rexy]] meets [[Tyrannosaur Buck|Buck]] and [[Tyrannosaur Doe|Doe]]]] |
||
| − | The T. rex then makes its second appearance in ''[[The Visitor Center]]''. After a harrowing climax, Dr. Harding and Jess make it outside, managing to hit the ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' with a few tranquilizer darts. Nima, now fully recovered, helps them drive away the predator by sending the jeep wheeling away, and the ''Tyrannosaurus'', now in a sedating, confused stupor due to the darts, follows the lone tour car. It would later be found to be missing the roof and badly damaged. |
||
| + | In the late Cretaceous period, Tyrannosaurus rex was the ancestor of dinosaurs like Rexy, Buck, and Doe. These individuals were cloned from this ancient species. While the original Tyrannosaurus rex was likely a solitary creature, capable of living and hunting alone, it is interesting to note that if a pair of T. rex encountered a lone individual, they could potentially socialize with it and even accept it into their group, forming a pack. It is possible that Rexy, who had been living on Isla Nublar without any contact with her own kind for many years, may not have had the opportunity to learn how to interact aggressively or peacefully with other T. rex. This means that when she encountered Buck and Doe, who were also clones of the same species, there was a chance for a calm and non-hostile interaction. It's important to consider that a lone Tyrannosaurus rex might be aggressive towards others of its kind due to territorial or resource competition, or for the protection of their young. However, in Rexy's case, she did not have any territory, resources, or young to defend, which may have contributed to the peaceful encounter with Buck and Doe. |
||
| + | ==Behind the Scenes== |
||
| − | In ''[[Did You Hear That?]]'' it appears in the clearing where Yoder, [[Oscar Morales]] and Nima crashed the helicopter. Yoder and Nima, along with the ''Parasaurolophus'' that the predator is chasing, run to the area near the water tower and the tunnels. The T. rex loses the ''Parasaurolophus'', but kills a loitering ''[[Velociraptor]]'', gaining access to another ''Parasaurolophus'' its pack had already killed. |
||
| + | ===''Jurassic Park'' (1993)=== |
||
| + | ====Design==== |
||
| + | [[File:Lawrence frog trex.jpg|thumb|Early design concept by Tim Lawrence]] |
||
| + | Early design work for the ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex entertained ideas not present in the final film. One early concept Spielberg considered was to give the dinosaurs frog-like features to show their origin as genetic amalgamations. Artist Tim Lawrence created an early head sculpt with the basis coming from toads. This was never meant to be the final design, as certain features like teeth were omitted, but just a basis to test the ideas. |
||
| + | [[Mark McCreery|Mark "Crash" McCreery]] created the design of the ''T. rex'' that was used in the film. McCreery was working on ''{{w|Terminator 2: Judgment Day}}'' when the late [[Stan Winston]] moved him from that project to create sketches of the ''T. rex'' to generate interest in the film for [[Universal Studios]].<ref name="Cinefex55p48">Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. ''Cinefex'', 55, p. 48.</ref> His first drawing was the ''T. rex'' running against a plain white background as a motion study. His second was of the ''T. rex'' in a jungle setting lifting its left leg high in an attack stance reminiscent of a bird of prey.<ref>''[[The Making of Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 20</ref> McCreery created the designs without a reference to go by, creating the drawings with what he remembered in his mind of then-current information and new paleontological findings. After these sketches were done, Winston showed [[Steven Spielberg]] what McCreery had created and Spielberg gave his suggestions for the design of the animal. He felt that the design depicted in McCreery's drawings should have longer legs to hold the weight of it and that the feet were too small and bird-like. Spielberg also felt that the forearms looked weak.<ref name="Cinefex55p48" /> |
||
| − | Yoder has to sneak past the ''Tyrannosaurus'' to retrieve the embryo can that he dropped. |
||
| + | [[File:Snapshot 23.png|thumb|right|300px|Character study by [[Mark Hallett]] from 1990.]] |
||
| + | Several paleoartists were contacted in 1990, notably to design the ''T. rex''. Among those consulted were [[Mark Hallett]], [[Gregory S. Paul]], and [[John Gurche]]. As his first assignment from production designer [[Rick Carter]], Mark Hallet created concept art of the ''T. rex'' breakout. Afterward, Hallett created concept art of the Tyrannosaur's attack on the explorers and then storyboards of the Tyrannosaur's attack from the driver's side view of one of the tour vehicles. Finally, he created a character study of the ''T. rex''.<ref>Hallet, Mark. (Spring 2013) Sketch me a Spitter! ''Prehistoric Times Magazine'', 105, pp. 47-48</ref> |
||
| + | Concept art of scenes featured of the ''T. rex'' by Craig Mullins,<ref>''[[The Making of Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 7</ref> David Negron,<ref name="David">''[[The Making of Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 9</ref> John Bell,<ref>''[[The Making of Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 13</ref> and Tom Cranham,<ref name="Cranham">''[[The Making of Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 10</ref> resemble Hallet's design. Paleontologist [[Gregory S. Paul]] created skeletal and muscle studies of the ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' to be used as the base form of the dinosaur.<ref name="AutoBio">[http://gspauldino.com/part4.html Gregory S. Paul: The Full Autobiography Part 4]. ''gspauldino.com''</ref><ref name="Vitae">[http://gspauldino.com/curriculum.html Curriculum Vitae - Gregory S. Paul: Books, Articles, Abstracts & Other Projects]. ''gspauldino.com''</ref> Paleoartist [[John Gurche]] also did concept art of the ''T. rex'', these concepts being its anatomy and reconstructions that were accurate for its time.<ref>Kartzman, Mark. [http://archive.is/uN6u John Gurche Interview] ''Artzar'' (archived from the [http://www.artzar.com/content/gurche/ original)]</ref> Paleontologist Dr. [[Robert Bakker]] sent the filmmakers diagrams of ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex teeth, but according to Bakker "the powers that be didn't like the real tooth shape" and used a different, inaccurate design for its teeth.<ref>Kushner, David. (January 17, 2012) [http://www.popularmechanics.com/culture/movies/a11747/scientific-advisors-to-the-stars/ Meet the Scientists Who Make Science Fiction Believeable]. ''Popular Mechanics''.</ref> The eyes of the ''T. rex'' were kept party by director [[Steven Spielberg]] because he felt it looked better when she was running toward the camera.<ref name="Zbrush">zbrushcentral.com - Interview: ILM on Jurassic World (February 3, 2016) Retrieved from http://www.zbrushcentral.com/showthread.php?198673-Interview-ILM-on-Jurassic-World</ref> |
||
| + | [[File:JurassicPark-TRexRampage.jpg|thumb|300px|left|The second concept art made of ''Tyrannosaurus'' by Mark "Crash" McCreery.]] |
||
| + | Winston and McCreery would spend months redesigning the ''T. rex'' multiple times until a finalized design was reached.<ref name="Cinefex55p48" /> When sculpting the 1/5 scale maquettes, Stan Winston and [[Mike Trcic]] spent time focusing on the design of the ''T-rex's'' head, with the maquettes going through over thirteen different head designs as according to [[Paul Mejias]], "[The dinosaurs] had to be perfect."<ref name="Sculpt">Duncan, Jody. (December 15, 2012) [https://www.stanwinstonschool.com/blog/jurassic-park-t-rex-sculpting-a-full-size-dinosaur# Jurassic Park's T-Rex - Constructing a Full-Size Dinosaur]. ''Stan Winston School'', excerpted from ''The Winston Effect: The Art and History of Stan Winston Studio''.</ref> Trcic created several anatomically accurate ''T. rex'' head sculpts as a potential design, but this would go unused in favor of a broader head and exposed front teeth.<ref>Hallet, Mark. (Spring 2013) Sketch me a Spitter! ''Prehistoric Times Magazine'', 105, pp. 48</ref> According to Gregory S. Paul, Trcic also used one of Paul's ''T. rex'' skeletals when designing the ''T. rex'',<ref name="PrehistoricTimes2">Morales, Bob. (April/May 1999) The PT Interview: Gregory S. Paul Part I. ''Prehistoric Times'', 35, p. 10. Retrieved from http://gspauldino.com/PTinterview1999.pdf</ref> but director [[Steven Spielberg]] and [[Stan Winston]] ordered the dinosaurs to receive alternations from the current scientific knowledge of the dinosaurs Paul created skeletals for to copyright their designs, even though Trcic wanted to strictly use Gregory S. Paul's diagrams.<ref>Paul, Gregory S. (Fall 2013) A Little More On Jurassic Park. ''Prehistoric Times'', 107, p. 46</ref><ref name="AutoBio" /><ref name="PrehistoricTimes2" /> However, Trcic has said that after many arguments with Winston over the design of the ''T. rex'', the ''T. rex'' design was "60% where [he] wanted it to be." McCreery then created another design of the ''T. rex'' based on the maquette.<ref>[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DAEoYe1MT5w Michael Trcic Discusses Creating the Jurassic Park T-Rex]. ''YouTube''</ref> |
||
| + | [[File:JurassicPark-TRexSide.jpg|300px|thumb|Concept art of a design of the ''Tyrannosaurus'' by McCreery from 1991.]] |
||
| + | Early concepts of the ''T. rex'' depicted her as having a green coloration with black striping.<ref name="David" /><ref name="Cranham" /><ref>Hallet, Mark. (Spring 2013) Sketch me a Spitter! ''Prehistoric Times Magazine'', 105, p. 49</ref> The final coloration of the ''T. rex'' chosen for the first film was a dark brown color. McCreery explained that the reasoning behind this was because an animal as large as ''T. rex'' would not need camouflage and that the team feared that too strong of coloration might make it look fake.<ref>Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. ''Cinefex'', 55, p. 73.</ref> A green coloration would later be used for the males in ''The Lost World: Jurassic Park'' and ''Jurassic Park III''. The design that "Crash" McCreery first created would later be colored and used in promotional material for ''Jurassic Park'' and its sequel ''The Lost World: Jurassic Park''. |
||
| + | ====Portrayal==== |
||
| − | [[File:T-rex.png|thumb|250px]] |
||
| + | ;Stop-motion to CGI |
||
| − | It makes its final appearance by the dock in the final climax of the game, eating [[Billy Yoder]]. It also eats [[Nima Cruz]] if the player chooses the ending to rescue the embryos. The climax culminates to the T. rex chasing Dr. Harding across the cargo bay before he finally makes it onto the boat, with [http://jurassicpark.wikia.com/wiki/Jess_Harding Jess] and with or without Nima. If the player chooses the opposite ending to rescue [http://jurassicpark.wikia.com/wiki/Jess_Harding Jess], it steps on the [[Barbasol]] can, destroying the embryos. It's very likely that the ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' was destroyed in the napalm bombing. |
||
| + | Originally, most of the wide shots of the dinosaurs were to be portrayed by {{w|go motion}} animation created by [[Phil Tippett]].<ref name="MakeJPDoc" /> With consultation from Mark Hallett,<ref>Hallet, Mark. (Spring 2013) "Sketch me a Spitter! An Artist Remembers Jurassic Park". ''Prehistoric Times Magazine'', 105, pp. 49</ref> Stefan Dechant had created digital animatics featuring a computer-generated ''T. rex'', but these were replaced by the go motion animatics created by [[Tippett Studio]].<ref>Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. ''Cinefex'', 55, p. 52.</ref> An animatic was even created of the breakout sequence featuring the go motion ''T. rex''. Tippit and his team sent Spielberg animation tests of ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex and ''Velociraptor''. Though a motion blur was added to make the stop motion dinosaurs more realistic, Spielberg felt that the movements of the dinosaurs were still jerky. Dennis Muren then suggested to Spielberg that [[Industrial Light and Magic]] create computer-generated full-sized dinosaurs. Interested, Spielberg requested a test be made featuring CGI dinosaurs.<ref name="MakeJPDoc" /> |
||
| + | [[File:Clay motion rex.jpg|thumb|left|300px|The go motion ''Tyrannosaurus''.]] |
||
| + | After ILM created a herd of ''Gallimimus'' skeletons running,<ref name="MakeJPDoc">[[The Making of Jurassic Park (documentary)|''The Making of Jurassic Park'' documentary]]</ref> Steve 'Spaz' Williams with support and assistance from Mark AZ Dippe, his friend and confidant, created a running ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex skeleton during off-hours and in-between assignments at ILM. The reference he used for the skeleton came from page 341 of Gregory S. Paul's 1988 book ''{{W|Predatory Dinosaurs of the World}}''.<ref>Failes, Ian. (April 4, 2013) [https://www.fxguide.com/featured/welcome-back-to-jurassic-park/ Welcome (back) to Jurassic Park]. ''fxgudie''.</ref> Spielberg was not fully convinced to use CGI for the dinosaurs until ILM made more tests featuring a fully fleshed ''T. rex'' and said ''T. rex'' chasing a herd of fully fleshed ''Gallimimus''.<ref name="MakeJPDoc" /> This skin was rendered by Stefan Fangmeier.<ref>''[[The Making of Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 137</ref> Though the dinosaurs were to be now CGI in the film, the stop motion animatics and tests would be used as a reference for the animatronic dinosaurs.<ref name="ReturntoJPDoc2" /> |
||
| + | ;Animatronics |
||
| − | In Dr. [[Laura Sorkin]]'s personal journal, she hypothesizes that the movement-based vision of the ''Tyrannosaurus'' was caused by Dr. [[Henry Wu]]'s [[Filling the sequence gaps|frog DNA insertion]] rather than being a natural feature of the animal. However, she also admits that the disability makes the animal safer to observe. |
||
| + | A full-sized ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex animatronic was created by [[Stan Winston Studio]] for the filming of the dinosaur's breakout. Taking two years to make, the animatronic was the first animatronic to be mounted on a motion simulator to achieve gross body movements and at the time was the largest animatronic the studio ever produced<ref>''[[The Making of Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 104</ref> only being surpassed by the ''Spinosaurus'' animatronic created for ''Jurassic Park III''.<ref name="StanWinstonSchool">Duncan, Jody. (September 29, 2012) ''[https://www.stanwinstonschool.com/blog/jurassic-park-iii-spinosaurus-animatronic Jurassic Park III's T-rex Killer: Spinosaurus]''. Stan Winston School of Character Arts.</ref> Powered primarily by hydraulics,<ref>Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. ''Cinefex'', 72, p. 73.</ref> a 1/5 scale telemetry device shaped like the dinosaur was used to provide the movements of the full-sized animatronic<ref name="ReturntoJPDoc2">''[[Return to Jurassic Park: Making Prehistory]]''</ref> with the eyes being radio controlled.<ref name="Page31" /> Another animatronic was also used for shots of its feet that was an underbelly on a rolling platform with hydraulic legs and tail.<ref name="Page31" /><ref name="Page107" /> Another prop was a separate head with extra detailing and added mechanics used for close-up photography.<ref name="Page31">''[[The Making of Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 31</ref> |
||
| + | There had been plans to create a full-sized sleeping ''T. rex'' that was later conceived as a miniature when Stan Winston proposed to the studio that the money that was to be used for this animatronic be used to create the full-sized ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex instead until the sleeping ''T. rex'' was scrapped altogether.<ref name="Cinefex55p72">Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. ''Cinefex'', 55, p. 72.</ref> Concept art was even created by "Crash" McCreery of this cut prop.<ref>[[Jurassic Park Topps trading cards|''Jurassic Park'' Topps trading cards]]: [[Topps/Card Set 1 P10 - Card Set 2 P1|#84 - Sleeping Tyrannosaurus]]</ref> Stan Winston Studio also considered using a 1/5 scale rod puppet before the full-sized animatronic was conceived.<ref name="Cinefex55p72" /> This concept would later be put to life for the sequel ''Jurassic Park III'', but only as a test.<ref name="JPIIIRodPuppet" /> Speilberg had also originally wanted the animatronic ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex to be a freestanding and that was able to walk until it was discovered that it was impossible and he realized how impractical it would be.<ref>Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. ''Cinefex'', 55, p. 48.</ref> |
||
| − | ===''The Lost World: Jurassic Park''=== |
||
| − | [[File:Tyrannosaurus-family.jpg|thumb|260px|The Tyrannosaurus family. ''([[The Lost World: Jurassic Park (film)|The Lost World]])'']] |
||
| − | A pair of ''Tyrannosaurus''; a male and a female, and a baby are present in [[The Lost World]]. [[Roland Tembo]] captures the infant to lure the male into the open so he can capture it. The infant is rescued by Dr. [[Sarah Harding]] and [[Nick Van Owen]], who then put a temporary cast on its broken leg. Unfortunately, the cries of the infant draw its parents to the research trailers. Dr. Harding releases the infant in hopes that the adults will leave, but they attempt to dispose of the invaders by pushing the trailers over a nearby cliff and into the sea. [[Eddie Carr|Eddie]] manages to keep them from falling, but the adults return unexpectedly, angered by his efforts to save them, and proceed to tear through the car and eat him. |
||
| + | The animatronics were filmed on set at Warner Brothers Studio Stage 16.<ref>''[[The Making of Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Jody Duncan]], p. 106</ref> For the filming of the attack sequence, the animatronic with legs <ref name="Page107">''[[The Making of Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 107</ref><ref name="ReturntoJPDoc2" /> and the insert head were used. The insert head, in particular, was manipulated by a highly poseable hydraulic-powered crane as well as man-power.<ref>Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. ''Cinefex'', 55, p. 76.</ref> |
||
| − | [[File:TLW-InfantT-Rex.jpg|250px|thumb|left|The infant ''Tyrannosaurus'' seen in The Lost World: Jurassic Park]] |
||
| + | There were troubles while filming the scene as both the animatronics began to shiver due to their latex skin absorbing the rain,<ref name="ReturntoJPDoc2" /> requiring the crew to dry the animatronics down after every shot.<ref>''[[The Making of Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 111</ref> Filming also received a major setback when the head-turn cylinder of the full-sized animatronic broke, though this was quickly repaired.<ref>Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. ''Cinefex'', 55, p. 79.</ref> Overall, shooting of the scene was finished four days ahead of schedule.<ref>''[[The Making of Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 112</ref> |
||
| − | They later pursue the group, now traveling with [[Peter Ludlow|Ludlow's]] party and kill a number of people. Roland manages to use a tranquilizer on the male and shoot him down, which is transported to [[San Diego]] on the ship S.S. ''Venture''. |
||
| + | In the original endings for ''Jurassic Park'', one raptor was to be crushed by one of the falling skeletons while the other would either be moved and crushed to the jaws of the ''T. rex'' skeleton by Dr. Grant using a crane or by Hammond shooting the raptor.<ref name="RTJPMP">''[[Return to Jurassic Park: Making Prehistory]]''</ref><ref name="TMOJP118">''[[The Making of Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 118. </ref><ref>Sharpio, Mark. (1993, August) In the Shadow of the Dinosaurs. ''Fangoria'', 27. Retrieved from http://www.jurassicworlduniverse.com/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/199308-fangoria-125.pdf</ref> Another ending would have also featured Hammond coming killing the first raptor with a bazooka while Dr. Grant used a crane to kill the remaining raptor-like one of the other ending.<ref>Freer, Ian (October 8, 2014) [http://www.empireonline.com/movies/features/steven-spielberg-special-effects/ Steven Spielberg And Special Effects]. ''Empire''.</ref>The ''T. rex'' was even scripted to die like her novel counterpart at one point.<ref>Nerdist Podcast - Episode 772: Kathleen Kennedy (December 16, 2015) Retrieved from http://nerdist.com/nerdist-podcast-kathleen-kennedy/</ref> These endings and her death were scrapped from the film because Spielberg believed the ''T. rex'' to be the star of the film alongside the smaller ''Velociraptor''.<ref name="TMOJP118" /> |
||
| − | Despite the being restrained a cage would barely allow it to move, the Rex breaks free and devours the crew during the journey and is accidentally released after the ship smashes into the dock. Dehydrated and hungry, the Rex rampages through the city in search of food and water, finding the latter in the form of a swimming pool and the former in the form of a pet dog. Although the dog's owners find the Rex after their son is awakened by its loud growl, we do not know if they are eaten or not. |
||
| + | Phil Tippit worked with ILM in post-production to create the dinosaur input device or DID for short; an armature like that seen in go motion models that could be manipulated by Tippit and his team of stop-motion animators.<ref>''[[The Making of Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 132</ref> Out of the four DIDs created, two were for ''T. rex'' while other two were for the raptors.<ref>Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. ''Cinefex'', 55, p. 58.</ref> The ''T. rex'' DIDs was only used for the road attack sequence while ILM created the rest of the shots featuring ''T. rex'' as Tippitt's team and ILM were originally going to work together until it was decided that both would be split into two teams.<ref>''[[The Making of Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 133</ref> The digital model for the ''T. rex'' received several changes from Spielberg that differed from the animatronic, these changes being a different arm length, larger and stockier feet, and a more streamlined jaw as well as adjustments to her eyes.<ref name="Zbrush" /> Years later, ILM would modify the ''T. rex'' model for lip-sync tests for the 1996 film ''{{w|Dragonheart}}''.<ref>Failes, Ian. (May 31, 2016) [http://www.cartoonbrew.com/feature-film/oral-history-ilms-dragonheart-20th-anniversary-140165.html An Oral History of ILM’s ‘Dragonheart’ On Its 20th Anniversary]. Cartoonbrew.</ref> |
||
| − | [[File:JPTLWRexRoarSanDiego.png|250px|thumb|San Diego in sight]] |
||
| + | ====Vocalizations==== |
||
| − | Doctors Ian Malcolm and Sarah Harding retrieve the infant from a secure facility that it was brought to via helicopter. They use it to lure the adult back to the S.S. ''Venture'', placing it in the cargo hold. Ludlow goes in to recapture it, but is trapped when the adult descends behind him and leaves the rest of the killing to the infant. Sarah manages to use a tranquilizer on the adult before an attempt was sent out to kill it, and it and its infant are transported back to [[Isla Sorna]] to rejoin the female. |
||
| + | The female roars were created from crocodiles, lions, alligators, dog, penguin, tiger, and elephant layered together.<ref name="MakeJPSound">''[[The Making of Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 144</ref><ref name="ReturntoJPDoc2" /> Whale blowholes were also used looped to create the sound of the dinosaur breathing.<ref name="MakeJPSound" /> The sound of the ''T. rex'' as it kills the ''Gallimimus'' was simply Rydstrom's dog, a {{w|Jack Russell Terrier}} named "Buster",<ref>Buachann, Kyle. (June 9, 2015) [http://www.vulture.com/2013/04/how-the-dino-sounds-in-jurassic-park-were-made.html You’ll Never Guess How the Dinosaur Sounds in Jurassic Park Were Made]. Vulture.</ref> playing with a rope toy.<ref name="MakeJPDoc" /> The footsteps of the ''T. rex'' were of redwood trees being cut down and falling to the ground.<ref name="ReturntoJPDoc2" /> The iconic high-frequency "scream" originates from a baby elephant that [[Gary Rydstrom]] and his team recorded. It was only recorded once creating this sound and the team tried to get the elephant to create the sound again, but it refused to do so. Because of this, Rydstrom used the same elephant sound for each take.<ref>Sullivan, Becky. (April 13, 2013) [http://www.npr.org/2013/04/13/177153801/jurassic-bark-how-sound-design-changed-our-imaginations Jurassic Bark: How Sound Design Changed Our Imaginations]. NPR</ref> This elephant sound was used for mid-range frequencies with an alligator's growl and tiger's roar added.<ref name="MakeJPSound" /> |
||
| + | ===''The Lost World: Jurassic Park'' (1997)=== |
||
| − | The number of deaths is not specified, but it seems that several were caused by panic rather than by the Rex itself. The ''T. rex'' did however, cause considerable material damage, most notably knocking a bus in a Blockbuster video store. |
||
| + | ====Design==== |
||
| − | The male ''Tyrannosaurus'' was 18 feet tall and 40 feet long. The female was 19.5 feet tall and 43 feet long. The infant was 3 feet tall and 6 feet long. |
||
| + | For the ''The Lost World: Jurassic Park'', a female, male, and juvenile ''Tyrannosaurus'' were set to appear in the film. In the digital storyboards by Stefan Dechant the male was depicted as either yellow and gray or as the same color as the female.<ref>''[[The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 26</ref> [[John Rosengrant]] later devised the green color scheme for the male.<ref>''[[The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 47</ref> One such concept by Rosengrant was a colored version of the 1991 ''T. rex'' concept art for the first film.<ref>[http://www.icollector.com/Mark-Crash-McCreery-and-John-Rosengrant-T-Rex-artwork-from-The-Lost-World-Jurassic-Park-II_i8632897 Mark “Crash” McCreery and John Rosengrant T-Rex artwork from The Lost World: Jurassic Park II] ''icollector.com''</ref> Another color scheme applied to this same concept art would be widely used in promotional material for the film. Even though the Buck was given a different skin color to differentiate it from the female, Stan Winston Studio was concerned that this would be difficult to see in low-light conditions. So [[Shane Mahan]] began to manipulate images of the ''T. rex'' from the first film, creating a series of eight head designs that he sent to Speilberg. The design chosen by Speilberg featured larger brows, a scarred face, and a neck wattle.<ref name="BuckScenes">''[[The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], pp. 45-46</ref> |
||
| − | {{-}} |
||
| + | [[Joey Orosco]] created the concept art for the juvenile.<ref>''[[The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 25</ref> The juvenile went through many changes in his color scheme, such as one of his maquettes depicting him as brown,<ref>''[[Making the 'Lost World']]''</ref> another maquette depicting him as bright green,<ref>[[File:2712801510 a87495402a.jpg|50px]]</ref> and one paint scheme of his animatronic depicting him as a duller green.<ref>Twitter@SWinstonSchool [https://twitter.com/SWinstonSchool/status/742845074833178624 From concept art to the real thing (with a lot of hard work in between by amazing artists) #30daysofdinosaurs]. (June 14, 2016)</ref> However, evidence in the film and promotional photos of the animatronic suggest that Junior is actually a mix of brown and green.<ref name="BrownJunior">[[File:The-lost-world-t-rex-baby.jpg|50px]][[File:Juniorbetter.png|50px]][[File:5467818 3 l-1-.jpg|50px]]</ref> The female also received a new skin color as well, her skin being lighter than the previous female that appeared in the first film.<ref name="Skin" /> However, promotional material depicted her as a darker brown and sometimes with a bluish tent to her head. |
||
| − | ===''Jurassic Park III''=== |
||
| − | [[File:DVDPlay 2009-04-24 19-59-06-13.jpg|thumb|left|''T. rex'' as it appears in JP3]] |
||
| + | ====Portrayal==== |
||
| − | In {{film|3}}, a male ''Tyrannosaurus'' was stumbled upon by Dr. [[Alan Grant|Grant]] and the others in the northwestern part of Isla Sorna. According to size-charts in the film's poster, the ''Tyrannosaurus'' from ''Jurassic Park III'' was 11 meter (37 feet) long and 4.5 meter (14.5 feet) tall. These measures are close to the best size estimates of ''Tyrannosaurus''. However, the animal is smaller than the (oversized) ''Tyrannosaurs'' from the previous films. |
||
| + | ;Animatronics |
||
| − | [[File:T-Rex_size.png|thumb|300px|''T. rex'' size (JP III)]] |
||
| + | [[File:Tyrannosaurparentsonset.jpg|thumb|300px|right|The two animatronic adults created for {{film|2}}.]] |
||
| + | For close-up shots in the film, two animatronics were used primarily to depict the tyrannosaur parents using the armatures of the full-body animatronic and insert-head of the first ''T. rex'', the female in particularly using the insert-head armature. Unlike the first full-sized ''T. rex'' animatronic, the animatronics for the parents was from head to mid-torso with arms and were mounted on rail powered dolly carts.<ref>''[[The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], p. 46</ref> This was done because Stan Winston Studio discovered there was no need to make a full-sized animatronic like in ''Jurassic Park'' as the audience could only see the head and half the body. Furthermore, the carts provided more mobility and freedom when compared to the motion platform.<ref>Duncan, Jody. (May 29, 2012) [https://www.stanwinstonschool.com/blog/the-lost-world-jurassic-park-2-t-rex-attack# The Lost World Jurassic Park 2's T-rexs]. ''Stan Winston School of Character Arts'', excerpted from ''The Winston Effect: The Art and History of Stan Winston Studio''.</ref> The most notable usages of the animatronics were when the parents approach the trailer and when they attack Eddie Carr.<ref name="ReturntoJPDocTLW" /> Two animatronics were used to portray the juvenile. One was a mixture of hydraulics and cables used when he was laying on his side while the other was remote controlled and used when someone was carrying him.<ref name="ReturntoJPDocTLW">''[[Return to Jurassic Park: Finding The Lost World]]''</ref> |
||
| + | ;From ''Pteranodons'' to San Diego |
||
| − | The Tyrannosaurus has a more green skin color. It is feeding on the corpse of a dead dinosaur. This is an allusion to [[Jack Horner]]'s idea that the ''T. rex'' was mostly a scavenger. When Grant and the others run away it immediately gave chase, possibly to protect its kill or chase the humans away. It crosses paths with the ''[[Spinosaurus]]''. The two carnivores engaged in a vicious battle and the ''T. rex'' seemed to have the upper hand in the fight until the ''Spinosaurus'' grabs the neck with its jaws, snapping its neck. The ''T. rex'' falls dead and presumably eaten by the ''Spinosaurus''. |
||
| + | In one of the original endings for ''The Lost World: Jurassic Park'', ''Pteranodon'' or ''[[Geosternbergia]]'' (then classified as a species of ''Pteranodon'') were to attack the rescue helicopter at the end of the film.<ref name="Survived" /> While at his vacation home in the Hamptons for the {{w|Independence Day (United States)|Fourth of July}}, director Steven Spielberg suddenly saw an image in his mind of a boy looking out of his bedroom to see a ''T. rex'' drinking from the family swimming pool. Prompted by the image he saw, Spielberg changed the ending to what is seen in the completed film<ref>''[[The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park (book)|The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park]]'' by [[Don Shay]] and [[Jody Duncan]], pp. 71-72</ref> and included the image he saw as the scene where the Buck approaches the house of young [[Benjamin]] and [[Benjamin's Parents|his family]]. In one concept of the ''T. rex'' being transported, it appears the mother was to be captured instead of the father as this ''T. rex'' is brown instead of green.<ref>[[File:Lostwolrdtrexconcept.jpg|50px]]</ref> |
||
| + | ====Vocalizations==== |
||
| − | ''Tyrannosaurus'' was later mentioned when [[Eric Kirby]] told Dr. Grant that he collected ''T. rex'' urine. Dr. Grant asked Eric how he collected the urine, Eric simply said that he did not want to know. |
||
| + | For the male, pigs and "weird Costa Rican mammals", mammals that Gary Rydstrom and his team recorded but never knew what their identities were, had a similar screech like the baby elephant used for the females and were used in place of the latter. The juvenile's vocalizations were of a baby camel crying for its mother.<ref name="Survived">''[[Return to Jurassic Park: Something Survived (...and came to San Diego)]]''</ref> The original ''T. rex'' roars were also reused for the female. |
||
| − | ===''Jurassic |
+ | ===''Jurassic Park III'' (2001)=== |
| + | ====The Replacement==== |
||
| − | In {{film|4}} ''Tyrannosaurus'' is one of the attractions of the [[Jurassic World (park)|new park]] on [[File:T-Rex_2.png|thumb|left|Jurassic World ''Tyrannosaurus'']] [[Isla Nublar (Movie canon)|Isla Nublar]]. The "''[[T. rex Kingdom]]''" is located at the center of the park, near the ''Jurassic World Lagoon''.<ref>[[Jurassic World map]].</ref> |
||
| + | In early logo designs for the film, ''Tyrannosaurus'' was to be featured like in the previous two films. Many of the logos had the same ''T. rex'' design used in the logos for the previous films, but there were different designs exhibited in the preliminary logos such as the ''T. rex'' with a more widened mouth,<ref>[[File:JPIII poster 19.PNG|50px]]</ref> the ''T. rex'' more upright and looking straight ahead,<ref>[[File:JPIII poster 21.PNG|50px]]</ref> and a full skeleton of ''T. rex'' roaring.<ref>[[File:JPIII poster 20.PNG|50px]]</ref> For ''Jurassic Park III'', the filmmakers wanted to have another dinosaur to replace ''Tyrannosaurus'' from the previous two films<ref name="MakeJP3">''[[The Making of Jurassic Park III]]''</ref> and searched through many candidates in the process.<ref name="Return">''[[Return to Jurassic Park: The Third Adventure]]''</ref> Eventually ''Spinosaurus'' was chosen after Paleontologist [[Jack Horner]] suggested ''Spinosaurus'' to the filmmakers as a replacement<ref name="JP3Website">[[jp3.jurassicpark.com]]</ref> and from the discovery of a Spinosaurus skull during the pre-production of the film.<ref name="StanWinstonSchool" /> |
||
| − | {{-}}[[File:Jurassic_world_tyrannosaurus_rex_by_hellraptor-d7yk47d.jpg|thumb|Jurassic World ''T. rex'' by Hellraptor]]Many fans speculate this ''Tyrannosaurus'' to be none other than [[Rexy]] herself given the notice of battle scars near her shoulder and head regions. It should be noted that these are the same places where [[The Big One]] had attacked Rexy in the first film. |
||
| + | During early development of the film, Stan Winston Studio created a 1/5 scale rod-puppet ''T. rex''. They filmed this rod-puppet in forced perspective to create several tests to see if they could prove a concept that would work.<ref name="JPIIIRodPuppet">[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LPVKkLcYuGw JURASSIC PARK III T-Rex Rod Puppet Tests & More.]</ref> This rod-puppet would ultimately go unused in the film. |
||
| − | == Jurassic Park Adventures == |
||
| − | ''Tyrannosaurus'' is featured in [[Jurassic Park Adventures: Prey|Prey]]. |
||
| + | ====T. rex versus ''Spinosaurus''==== |
||
| − | ==Video games== |
||
| + | [[File:DB8E1DCF-7146-413E-ACCE-8280A1A4062B.png|thumb|right|300px|The ''Spinosaurus'' and ''Tyrannosaurus'' animatronics on set.]] |
||
| − | ''Tyrannosaurus'' has appeared in all Jurassic Park games. Listed below is a list of notable games featuring the dinosaur. |
||
| + | Director [[Joe Johnston]] created the famous Spino vs ''T. rex'' as an homage to {{w|Ray Harryhausen}}'s go motion dinosaurs and wanted to recreate a modern version of those fights.<ref>Berry, Mark F. (January 1, 2005) ''The Dinosaur Filmography'', p. 172. (Google Books) Retrieved from https://books.google.com/books?id=KoeACgAAQBAJ&dq=joe+johnston+ray+harryhausen&source=gbs_navlinks_s</ref> In one draft of the script the carcass the ''Tyrannosaurus'' was eating was a sauropod<ref>[[Jurassic Park III Film Script|''Jurassic Park III'' film script]]: [[Jurassic Park III Film Script#Scene 40: Int. Plane|Scene 40: Int. Plane]]</ref> when the actual prop used in the film is the ''Parasaurolophus'' carcass used in ''The Lost World: Jurassic Park'' repainted<ref>This can be proven due to it having exposed ribs like the dead ''Parasaurolophus'' made for TLW and has a greenish skin color with a dark green splotch on its back like the repainted later.</ref> and the carcass itself is left unidentified in the film. |
||
| − | [[File:SimJP 2008-03-19 21-57-55-09.jpg|thumb|left|A re-skinned ''T. rex'' in JPOG]] |
||
| + | For the battle, the animatronic of the Buck was refurbished.<ref>[[Jody Duncan]] writes that the ''T. rex'' animatronic was simply one of the Tyrannosaurus built for ''The Lost World: Jurassic Park'' albeit refurbished. The identity of the TLW Tyrannosaur that was reused for ''Jurassic Park III'' is the Buck due to the presence of a scar on the side of its face, neck wattle, more prominent brows, and bearing dark yellow striping on its neck and upper back.</ref> Due to how powerful the mechanical Spinosaurus was, the Spino destroyed the ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex with one final blow that broke its neck which in turn caused its head to collapse, releasing hydraulic fluid that John Rosengrant described as being "almost like blood spewing". Rosengrant further described the destruction of the animatronic as "[A] really sad ending to a long night of shooting".<ref name="StanWinstonSchool" /> Over 20 seconds of footage of the fight, particularly of the animatronics, was cut from the film.<ref>Goldwasser, Dan. (July 9, 2001) [http://www.soundtrack.net/content/article/?id=75 Don Davis - Interview]. Soundtrack.net.</ref> Despite this, a shot of the animatronic fight where the Spinosaurus slaps the Tyrannosaur was still present in the theatrical trailer.<ref>[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TY_W3Zqcx3w YouTube - Jurassic Park III (2001) Theatrical Trailer]</ref> For the CG ''T. rex'', the model of the Buck from the previous film was reused as a basic framework, but when it was all finished, it was essentially a new model according to Tim McLaughlin.<ref>https://i.imgur.com/etUow3z.jpg Cinefex #87, pg. 37</ref> New geometry was created for its surfaces so that it would work better in ILM's simulations. New animation controls were added as well that were up to date at the time the computer graphics were created for the film and the model's {{w|UV mapping|UV Maps}} were reworked, though originally the ones from ''The Lost World'' were to be used.<ref>Deckel, Larry. (October 2001) Jurassic Park III: Bigger, Faster, Meaner. ''Cinefex'', 87, p. 37.</ref> |
||
| − | ===[[Jurassic Park (arcade game)]]=== |
||
| − | ''Tyrannosaurus'' is featured in the arcade version of [[Jurassic Park (film)|Jurassic Park]]. In the game, the player encounters the T. rex three times within the game and is a boss at all times. In Area one the ''Tyrannosaurus'' is the first dinosaur you encounter and is chasing you while you have to shoot at her head. At the end of Act two you encounter it again and you must defeat it the same way as the first time by shooting at its head, this time however the rex is harder to kill and has a health bar. At the end of the game in Act four you encounter the ''T. rex'' along with a second and you must defeat them at the same time by shooting at their heads, just like the previous time both of them also have health bars. |
||
| − | === |
+ | ===''Jurassic World'' (2015) and ''Fallen Kingdom'' (2018)=== |
| + | [[File:JURASSIC-WORLD-Vfx-Break(4).jpg|thumb|300px|left|The ''Jurassic World'' CG model.]] |
||
| − | ''Tyrannosaurus'' appears in the arcade adaptation of The Lost World: Jurassic Park; both the male and the female ''<nowiki>T. rex'</nowiki>''s from the film served as the game's bosses, the female as first boss in Stage 1 and the male as the last boss in Stage 5 after the female. The baby ''Tyrannosaurus'' is featured in Stages 4 and 5. |
||
| + | ''Jurassic World'' saw the return of the ''T. rex'' that appeared in ''Jurassic Park''. Director Colin Trevorrow described the film "This is [the Tyrannosaur's] ''{{w|Unforgiven}}''."<ref name="ScreenRant">Sciretta, Peter. (April 29, 2015) [http://www.slashfilm.com/jurassic-world-performance-capture/ Original T. rex Returns in ‘Jurassic World,’ This Film “Is Her Unforgiven”]. ''Slashfilm''.</ref> The ''T. rex'' model was created by Steve Jubinville and the director aimed to make the model look as close as possible to its design in the first film.<ref>[http://www.stevejubinville.com/-jurassic-world-2015/622krp35xjoxmd0105ogmwzk0xn1zc Jurassic World] stevejubinville.com.</ref> The ''Jurassic World'' ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex was made to look older by giving her the scars she received from the end of ''Jurassic Park'' as well as tightened skin. The ''T. rex'' was primarily portrayed with performance capture technology rather than life-sized animatronics.<ref name="ScreenRant" /> |
||
| + | [[File:8LpsavP.jpg|thumb|300px|''T. rex'' animatronics on set for {{film|5}}]] |
||
| − | ===[[Jurassic Park: Chaos Island]]=== |
||
| + | In {{film|5}}, the ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' was recreated through a mixture of traditional animatronics and CGI.<ref name="JWFK">{{film|5}}</ref> |
||
| − | ''Tyrannosaurus'' appears in Jurassic Park: Chaos Island, as one of the strongest dinosaurs and the hardest to kill. The baby ''T. rex'' is also featured in two of the missions. In the bonus mission taking place during the [[San Diego incident]], the player plays as the ''Tyrannosaurus rex''; who oddly in the game is female, instead of male. The rex in the game resembles the [[The Lost World Series 1/Bull T-Rex|Bull ''T. rex'']] from [[The Lost World Series 1]] toyline. |
||
| + | ===''Dominion'' (2022)=== |
||
| − | ===[[The Lost World: Jurassic Park (video game)]]=== |
||
| − | ''[[The Lost World: Jurassic Park (video game)#Tyrannosaurus|Tyrannosaurus]]'' is featured in the console adaptation of the [[The Lost World: Jurassic Park]] film. It serves as both a playable character and the final boss of the game. |
||
| + | ==Trivia== |
||
| − | ===[[Warpath: Jurassic Park]]=== |
||
| + | ===Cultural Impact=== |
||
| − | [[File:TREXwarpathJP.jpg|thumb|''Tyrannosaurus'' from Warpath: Jurassic Park, in its default color scheme (blue)]] |
||
| + | In popular culture, ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' has an iconic status shared by few other species, helped in no small part by the prominent role of the ''T. rex'' in all five films in the ''[[Jurassic Park]]'' franchise. The design of the Jurassic Park franchise's ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' is a notably popular way to depict ''T. rex'' in media.<ref>[http://www.bbc.co.uk/nature/life/Dinosaur Dinosaurs]. ''www.bbc.co.uk''.</ref> |
||
| − | ''Tyrannosaurus'' is featured in the video game [[Warpath: Jurassic Park]]. Its attack patterns were the same as ''[[Acrocanthosaurus]]'' and ''[[Cryolophosaurus]]'' and has 3 colors: ''blue, green, and blue with orange stripes''. Its arena was [[S.S. Venture|Freighter Deck]]. |
||
| − | {{-}} |
||
| − | ===[[Jurassic Park: Trespasser]]=== |
||
| − | [[File:Dino007.jpg|thumb|''T. rex'' (male according to game files) in Trespasser.]] |
||
| − | [[File:Dino008.jpg|thumb|left|''T. rex'' (female according to game files) in Trespasser.]] |
||
| + | Mike Trcic expressed disappointment with the popularity of this design in an interview with [[Shannon Shea]] (who worked with Trcic on ''Jurassic Park''). In the interview, he said regarding how popular the design had become, “Whenever I search Google images for a Tyrannosaurus Rex [sic], most of the art I see is based on the original JP Rex. It’s a shame that people just accept that somehow it IS what a T-Rex [sic] looked like. It’s limiting because unless someone can travel back 65 million years, how can anyone be completely sure?”<ref>Shea, Shannon. (June 11, 2015) [https://filmschoolrejects.com/how-we-made-the-iconic-t-rex-of-jurassic-park-7bbadfa397a0#.9yi8m2wm6 How We Made The Iconic T-Rex of Jurassic Park]. ''Filmschool Rejects''.</ref> |
||
| + | The vocalizations that were created by Gary Rydstrom are also a popularly used sound effect. ''Jurassic World'' sound designer Al Nelson said regarding how famous its roars were in the films: "The ''T. rex'' is one of the most iconic sounds in all of film history. Every sound designer knows it. Almost any kid knows it. When you hear it, you're like 'That's the ''T. rex''!'"<ref>[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8SdT97vj00s Making Tyrannosaurus Rex Sound]. ''Youtube''</ref> |
||
| − | ''"Tyrannosaurus Rex--Tyrant Lizard. They reigned for 25 million years; we grew seven of them, the seven rulers of the island."'' |
||
| + | ===Paleontology=== |
||
| − | ''-John Hammond'' |
||
| + | Section for real-life paleontology |
||
| + | Like other tyrannosaurids, ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex had very short arms with only two fingers. Despite the limbs' size, each were able to bench-press about 400 pounds. Although these were probably nearly useless while hunting, its jaws were not: ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex has an enormous skull armed with teeth the size of bananas. Unlike the teeth of most theropods, the teeth of tyrannosaurids are very thick and capable of crushing bones and with a bite force of a minimum of 4 tons of force and probably more, crushing bone, ripping flesh, and bursting blood vessels of the victim. The skull and neck bones show that ''T. rex'' had the largest neck muscles of any meat-eating dinosaur. It probably used its strong neck to twist and pull off big chunks of meat that it grasped with its jaws while supporting the huge head. ''Tyrannosaurus'' rex could bite with extremely strong force - one fossilized skeleton shows that it crushed and swallowed the bones of a smaller plant-eating dinosaur while another shows a ''T. rex'' coprolite with the crushed frill of a ''Triceratops''. Additionally, in ''[[Jurassic World: Alive]]'', the Generation 2 ''Tyrannosaurus'' is referred to as ''Tyrannosaurus magnus'', which scientists have considered a separate genus, ''{{W|Zhuchengtyrannus}}''.<ref name="guide" /> |
||
| − | In [[Jurassic Park: Trespasser]], ''Tyrannosaurus'' is an enemy, being the most powerful adversary in the game. It is invincible, unless being killed by the Toxic Rifle, or other hidden weapons. It is said that InGen made seven T. rex, meaning seven kings of the prehistoric world, each of which would be faced at one point during the course of the game. The colors of some of the ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' were based on ''The Lost World: Jurassic Park''. It is first seen in the [[Industrial Jungle]] and last seen in [[The Ascent (Part I)|The Ascent's first part]]. The ''Tyrannosaurus'' in Ascent 1 is called the "Alpha ''Tyrannosaurus''" according to ingame files. The Alpha ''Tyrannosaurus'' also makes an appearance in the Trespasser Demo as well. In addition, another ''Tyrannosaurus'' skin didn't make the cut. This ''Tyrannosaurus'' was a brighter green than the normal green T. rex. It is unknown why this green ''Tyrannosaurus'' was scrapped, but it might have had to do with the fact that the skin was too high in quality. |
||
| + | A 2016 study suggested that T. rex probably didn't roar, but most likely cooed, hooted, and made deep-throated booming sounds like the modern-day emu. |
||
| − | ===Jurassic Park: Operation Genesis=== |
||
| − | [[File:Jurassic Park Operation Genesis - Free Download PC Games 5.jpg|thumb|200px]] |
||
| − | ''see [[Tyrannosaurus rex/Operation Genesis]]'' |
||
| + | ==Gallery== |
||
| − | ''Tyrannosaurus'' is one of the main dinosaurs in the game [[Jurassic Park: Operation Genesis]]. It is a 5-star carnivore, and is described as possibly the most powerful dinosaur in the game. It will devour guests, swallowing the guest whole after first shaking them around violently, making it mirror the death of Gennaro in the [[Jurassic Park|first film]]. The ''T. rex'' in the game is green, reflecting the appearance of the specimen seen in ''Jurassic Park III''. The ''<nowiki>Tyrannosaurus'</nowiki>'' sociability among others of its kind is usually isolated, when another Rex encounters another they engage in combat against one another for territorial rights which eventually leads to death. It is seldom seen where both dinosaurs coexist with one another. |
||
| + | ===Images=== |
||
| + | <gallery> |
||
| + | When Dinosaurs Ruled The Earth.jpg|''Tyrannosaurus'', as she appears in {{film|1}}. |
||
| + | Tyrannosaurus-family.jpg|A family of ''Tyrannosaurs'' in {{film|2}}. |
||
| + | Tyrannosaurus rex.jpg|The second bull ''Tyrannosaurus'' in {{film|3}}. |
||
| + | Jurassicworld-trex-ending-1.jpg|''Tyrannosaurus'', as she appears in {{film|4}}. |
||
| + | 993d8402-1a7f-404b-8bde-8223a82b2483 (2).png|''Tyrannosaurus'', as she appears in {{film|5}}. |
||
| + | Dominion rex9.png|''Tyrannosaurus'', as she appears in ''[[Jurassic World: Dominion]]'' |
||
| + | 4D5535C1-E093-49E3-A7C7-A51739093C86.jpeg|Tyrannosaurus in [[Warpath: Jurassic Park]] |
||
| + | Tlurrg.png|A ''Tyrannosaurus'' in 2004's ''[[Jurassic Park: Operation Genesis]]''. |
||
| + | T-RexJW.jpg|Main Generation of ''Tyrannosaurus'' in ''[[Jurassic World: The Game]]''. |
||
| + | Screenshot 20191102-004157.png|Second Generation of ''Tyrannosaurus'' in ''Jurassic World: The Game'' |
||
| + | Lego5.jpg|The ''Tyrannosaurus'' in ''[[LEGO Jurassic World (game)|LEGO Jurassic World]]''. |
||
| + | T-rex.png|''Tyrannosaurus'' as she appears in ''[[Jurassic Park: The Game]]''. |
||
| + | JWETyrannosaurus.png|The base skin of ''Tyrannosaurus'' in ''[[Jurassic World Evolution]]''. |
||
| + | Trexalive.png|Main generation of ''Tyrannosaurus'' in ''[[Jurassic World: Alive]]''. |
||
| + | Gen 2 Tyrannosaurus JWA.PNG|Second generation of ''Tyrannosaurus'' in ''Jurassic World: Alive''. |
||
| + | TyrannosaurParkBuilder.jpg|A ''Tyrannosaurus'' in ''[[Jurassic Park III: Park Builder]]''. |
||
| + | TyrannosaurMiniParkBuilder.jpg|A "Mini" ''Tyrannosaurus'' in ''[[Jurassic Park III: Park Builder]]''. |
||
| + | TyrannosaurusRexJurassicBattles.png|''Tyrannosaurus'' card from "Jurassic Battles." |
||
| + | Screenshot-2019-02-22 00.38.30.png|''Tyrannosaurus'' in ''[[Jurassic Park: Explorer]]'' |
||
| + | T-Rex in TLWJP Gear game.jpg.png |
||
| + | JPI Tyrannosaurus.png |
||
| + | JPI Dinotyrannus.png |
||
| + | JWD Rexy next to a car .png |
||
| + | JWD Rexy Roar.png |
||
| + | Jurassic-World-Dominion-Prologue-Ancient-Rexy.jpg |
||
| + | Rex and Giga Roar .png |
||
| + | File:GigaVsRexstandoff.png.png |
||
| + | Giga attacking a Rex.png |
||
| + | JWD Giganotosaurus prologue 4.png |
||
| + | JWDprologue 112.png |
||
| + | Dead Feathered Rex Eye.png |
||
| + | </gallery> |
||
| + | ===Vocalizations=== |
||
| − | ===Jurassic Park III: Park Builder=== |
||
| + | [[File:Trex.ogg|noicon|]] |
||
| − | [[File:TyrannosaurParkBuilder.jpg|thumb|''Tyrannosaurus'' from Jurassic Park III: Park Builder]] |
||
| − | [[File:TyrannosaurMiniParkBuilder.jpg|thumb|Mini. ''Tyrannosaurus'' from Jurassic Park III: Park Builder]] |
||
| − | Two Tyrannosaurs can be created in the GBA game ''[[Jurassic Park III: Park Builder]]''. |
||
| + | ==Appearances== |
||
| − | *''Tyrannosaurus'': 12 meter |
||
| + | {{Scroll| |
||
| − | *"Mini" ''Tyrannosaurus'': 0.7 meter |
||
| + | *{{film|1}} (<small>First appearance</small>) |
||
| + | *{{film|2}} |
||
| + | *{{film|3}} |
||
| + | *''[[Jurassic Park: The Game]]'' |
||
| + | *{{film|4}} |
||
| + | *''[[Jurassic World: Camp Cretaceous]]'' |
||
| + | *{{film|5}} |
||
| + | *{{film|6}} |
||
| + | ===See also=== |
||
| − | The smaller ''T. rex'' is probably a nod at the ''[[Baby T. rex]]'' from TLW. |
||
| + | ====Novels==== |
||
| − | {{-}} |
||
| + | *[[Tyrannosaurus rex/Novels|''Tyrannosaurus'' in the Jurassic Park novels]] |
||
| − | ===''Jurassic Park: Builder''=== |
||
| − | [[File:Tyrannosaur JPbuilder.jpg|thumb|''Tyrannosaurus'' from Jurassic Park: Builder.]] |
||
| − | ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' is one of the available dinosaurs in the simulation game ''[[Jurassic Park: Builder]]''. |
||
| − | {{-}} |
||
| − | ==Toy Lines== |
||
| − | ''T. rex'' has appeared in all toy lines. |
||
| − | <gallery> |
||
| − | ArcticTyrannosaur.jpg |
||
| − | CanyonTrexCamoX.jpg |
||
| − | TREXjp2K9.jpg |
||
| − | HatchlingTREX2K9.jpg |
||
| − | LavaTREXtoy.jpg |
||
| − | SwampTREXtoy.jpg|Swamp ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' from the CamoXtreme toyline (Image courtesy of JPToys.com) |
||
| − | TREX2009Bull.jpg|Large ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' from the Jurassic Park 2009 toyline (Image courtesy of JPToys.com) |
||
| − | TREXmini2009one.jpg|''Tyrannosaurus rex'' mini-figure 1 from the Jurassic Park 2009 toyline (Image courtesy of JPToys.com) |
||
| − | TREXmini2009two.jpg|''Tyrannosaurus rex'' mini-figure 2 from the Jurassic Park 2009 toyline (Image courtesy of JPToys.com) |
||
| − | TREXmini2009three.jpg|''Tyrannosaurus rex'' mini-figure 3 from the Jurassic Park 2009 toyline (Image courtesy of JPToys.com) |
||
| − | 24263.jpg|Custom Bull ''T. rex'' |
||
| − | </gallery> |
||
| − | == |
+ | ====Games==== |
| + | *[[Tyrannosaurus rex/JW: TG|''Tyrannosaurus'' in Jurassic World: The Game]] |
||
| − | <gallery widths="190"> |
||
| − | + | *[[Tyrannosaurus rex/Operation Genesis|''Tyrannosaurus'' in Jurassic Park: Operation Genesis]] |
|
| − | + | *[[Tyrannosaurus rex/Builder|''Tyrannosaurus'' in Jurassic Park: Builder]] |
|
| − | + | *[[Tyrannosaurus rex/JW: E|''Tyrannosaurus'' in Jurassic World: Evolution]] |
|
| + | *[[Tyrannosaurus rex/JW: A|''Tyrannosaurus'' in Jurassic World: Alive]] |
||
| − | </gallery> |
||
| − | == |
+ | ====Individuals==== |
| + | *[[Rexy (movie canon)|Rexy]] |
||
| − | [[Tyrannosaurus rex/Gallery]] |
||
| + | *[[Tyrannosaur Buck]] |
||
| − | |||
| + | *[[Tyrannosaur Doe]] |
||
| − | ==Trivia== |
||
| + | *[[Junior]] |
||
| − | *It is commonly believed that the ''Tyrannosaurus'' was the main antagonist of the film, but this is incorrect; the raptors were the true antagonists. The ''T. rex'' was merely an anti-hero. However, she can also be considered the star dinosaur, as Spielberg actually altered the ending prior to filming to include the ''T. rex'', knowing the audience would be disappointed if she did not return one last time. |
||
| + | *[[Tyrannosaur Bull]] |
||
| − | *The face of the Buck is adorned with many facial scars and many of the teeth in his mouth are broken or missing. This is indicative towards the animal participating in fights for mating rights or dominance. |
||
| + | *[[Big Eatie]] |
||
| − | *It's curious that Roland wishes to hunt the ''Tyrannosaurus ''Buck when the female ''Tyrannosaurus'' is actually larger. This could possibly stem from that fact that Roland is a professional hunter and in sport hunting it is the male that is prized for its size and adornment and Roland did not know that it is the female that is holds the size. |
||
| + | *[[Little Eatie]] |
||
| − | *The ''T. rex'' animatronic in ''Jurassic Park III'' was actually the same animatronic for the Buck in ''The Lost World: Jurassic Park''. Stan Winston Studios repainted the animatronic lighter colors in order to represent a sub-adult individual, however they can both still be recognized as the same robot by the facial scaring on the right side of the muzzle. |
||
| + | }} |
||
| − | == |
+ | ==References== |
| + | {{Refbox}} |
||
| − | ''[[Tyrannosaurus rex/Media|Click here]] for images and videos related to this article.'' |
||
| − | {{-}} |
||
| − | == |
+ | ==Navigation== |
| + | {{FilmCanonSpeciesNavbox}} |
||
| − | <references /> |
||
| + | [[Category:Jurassic Park (film) Animals]] |
||
| − | {{JPI Dinosaurs}} |
||
| + | [[Category:The Lost World: Jurassic Park Animals]] |
||
| − | {{JPII Dinosaurs}} |
||
| + | [[Category:Jurassic Park III Animals]] |
||
| − | {{JPIII Dinosaurs}} |
||
| + | [[Category:Jurassic World Animals]] |
||
| − | {{JPIV Dinosaurs}} |
||
| + | [[Category:Jurassic World: Camp Cretaceous Animals]] |
||
| − | {{Warpath dinosaurs}} |
||
| − | [[Category:Jurassic |
+ | [[Category:Jurassic World: Fallen Kingdom Animals]] |
| − | [[Category:Jurassic |
+ | [[Category:Jurassic World: Chaos Theory Animals]] |
| − | [[Category: |
+ | [[Category:Jurassic World: Dominion: The Prologue Animals]] |
| − | [[Category: |
+ | [[Category:Jurassic World: Dominion Animals]] |
| − | [[Category: |
+ | [[Category:Tyrannosaurus Pages]] |
| − | [[Category: |
+ | [[Category:Holoscape Animals]] |
| − | [[Category: |
+ | [[Category:Film Canon Species]] |
| − | [[Category:Tyrannosaurus rex]] |
||
| − | [[Category:Jurassic World dinosaurs]] |
||
Latest revision as of 20:03, 13 April 2024
| Introduction | Movies | Novels | Games | Toys | Books | Comics | Theme Parks |

|
"'Ooh, ah,' that's how it always starts. But then later there's running and screaming."
This page contains spoilers from an upcoming, or newly released installment of the Jurassic Park franchise. If you don't want spoilers, leave the page! |
This article refers to Tyrannosaurus in the Jurassic Park film canon. You may be looking for the novel canon.
- "Somewhere on this island is the greatest predator that ever lived."
- —Roland Tembo(src)
Tyrannosaurus rex, commonly known as T. rex, is a species of theropod dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous Period, 72 to 66 million years ago. Arguably the most famous species of dinosaur, T. rex lived in what is now North America, alongside species such as Ankylosaurus, Edmontosaurus, Pachycephalosaurus, Alamosaurus, Nanotyrannus, Triceratops, and Torosaurus. Tyrannosaurus rex was among many dinosaur species cloned by InGen and settled on the Costa Rican islands of Isla Sorna and Isla Nublar, for use as an attraction for Jurassic Park, and later, Jurassic World.
An apex predator capable of reaching thirteen meters in length, Tyrannosaurus rex was the largest species of Tyrannosaurid, and was intended to be the star attraction of John Hammond's vision for the original Jurassic Park.[1][2] During the Isla Nublar Incident in 1993, a female T. rex escaped from her enclosure, and became wild on the island.[2][3] Seven Tyrannosaurs existed on Isla Sorna, an island in the Muertes Archipelago originally used by InGen as a cloning facility for their dinosaurs. A family unit consisting of an adult male, an adult female and an infant were encountered during the Isla Sorna Incident in 1997, during which the male was captured and brought to San Diego, where it was intended to be used in the failed park, that Hammond had originally envisioned before acquiring Isla Nublar. The animal promptly escaped and wreaked havoc on the city, before being returned to Site B.[4] Three years later, another male Tyrannosaur was encountered on Isla Sorna, where it fought and was killed by a Spinosaurus.[5] Sometime in 2016, two female Tyrannosaurus rexes were involved in an incident with the kids of Camp Cretaceous on an island owned and operated by Mantah Corp.
The individual from the original park was eventually captured in 2002 and placed in captivity in Jurassic World on Nublar, residing in T. rex Kingdom. During the climactic events of the 2015 Jurassic World Incident, it was released from captivity and fought and helped defeat, the genetically modified hybrid Indominus rex.[6] This same T. rex became wild once more, though became threatened three years later during the volcanic eruption of Mount Sibo.[7] Before Mount Sibo erupted, many dinosaurs were brought off the island, including the T. rex, to be auctioned off at the Lockwood Manor. The T. rex, along with many other dinosaurs, ended up being released into the wild.
| Wikipedia has a more detailed and comprehensive article on Tyrannosaurus rex/Films |
History
In the Past
A later flashback in the Cretaceous showed that a feathered Tyrannosaurus rex appeared in prehistoric times where it was clashed against a Giganotosaurus, but it was killed after the battle. A mosquito lands on and bites the dinosaur's right side of the snout, giving the future scientists of Jurassic Park the chance to create Rexy, the modern descendant of this very same T. rex.
Isla Nublar Incident & Aftermath (1993)
- "We have a T. rex!"
- —John Hammond, to Ellie Sattler and Alan Grant.(src)
Seven Tyrannosaurus rex were cloned by InGen scientists in their compound on Isla Sorna, circa 1990.[4][5][8] A female Tyrannosaurus rex was transported to Isla Nublar to star as the main attraction of Jurassic Park, inhabiting the Tyrannosaur Paddock.[2] The paddock was originally intended to be inhabited by an adult, and a juvenile Rex, though it is unknown if a juvenile was ever transported there.[9]
A Tyrannosaurus rex skeleton was also on display in Jurassic Park's Visitor Center along with the skeleton of an Alamosaurus.

The Tyrannosaurus breaks out of its paddock during the Isla Nublar Incident.
Nublar's Tyrannosaurus rex was supposed to have been seen by InGen's endorsement team on their tour of Jurassic Park. However, despite attempts by Ray Arnold to lure her out of her paddock with a live goat, it did not originally reveal herself to the visitors.[2] When Dennis Nedry disabled most of Jurassic Park's security with a sophisticated virus, it was one of the dinosaurs that were able to roam the island freely. One of the embryos Nedry stole from the Cold Storage Room was Tyrannosaurus rex.[2] Upon eating the goat that was left for her, the Tyrannosaur escaped her exhibit and attacked the endorsement team, who were stranded near her paddock, eating Donald Gennaro. After pushing the tour vehicle of Lex and Tim Murphy off a cliff with Tim inside the vehicle, she attacked Dr. Ellie Sattler and Robert Muldoon who were searching for the survivors. After a short chase, she gave up, though.[2]
The next day, during Grant’s, Tim’s, and Lex’s continued trek to the Visitor Center, they found themselves in the Gallimimus Enclosure, and witnessed a stampeding herd of Gallimimus. They ran alongside the dinosaurs momentarily before hiding behind a fallen log. The T. rex suddenly crashed through the nearby bushes next to the stampede stumbling a Gallimimus. This Gallimimus tried to run away, but was too slow to react, and the Tyrannosaur lunged at it, catching the dinosaur in her jaws before proceeding to shake the Gallimimus to death. Dr. Grant, Lex, and Tim watched in amazement as the T. rex started to feast on the carcass. Lex begged Dr. Grant for them to go, to which Grant obliged. However, Tim continued to stare in fascination and so had to be forcibly taken away by Dr. Grant.[2] She never fully consumed this Gallimimus and its remains were still present in the location where it had died by October 6, 2002, over a decade later. Her roar was later heard from afar when Dr. Grant and the kids were trying to get through the deactivated electric fence, prompting them to climb over.[10]
The T. rex was seen later that day when she had come through the hole in the wall and grabbed a Raptor from mid-air just as it was to pounce on the humans and crushed it in her jaws. Using the distraction that she provided, the humans fled. Meanwhile, another Raptor that pursued the group through the Visitors Center pounced on the larger theropod. She snapped at her but could not reach her as the raptor continued to rip and tear madly. Rolling her head, the Raptor fell into the T. rex's mouth where she was killed and then thrown against the Tyrannosaurus rex skeleton and the T. rex let out a mighty bellow in triumph as the "When Dinosaurs Ruled the Earth" sign fell to the ground.[2]
In the aftermath of the incident, the T. rex went wild and lived on Isla Nublar for about a decade,[8][11] probably surviving off any of the herbivorous dinosaurs that managed to survive the incident.
San Diego Incident (1997)
- "I'm trying to change 100 years of entrenched dogma. Dinosaurs were characterized very early on as vicious lizards. There's a great deal of resistance to the idea of them as nurturing parents. Robert Burke said that the T. rex was a rogue, who would abandon its young at the earliest opportunity... I know can prove otherwise."
- —Dr. Sarah Harding, to Ian Malcolm during the Isla Sorna Incident(src)
The Tyrannosaurus rex on Isla Sorna became wild after Hurricane Clarissa struck the island, soon after the abandonment of Isla Nublar. They were freed by the workers on the island before they fled. As with the T. rex on Nublar, to counter the Lysine contingency, T. rex and the other carnivorous dinosaurs ate herbivores who in turn ate lysine-rich plants as one of their sources of lysine.[4] Tyrannosaurus rex had varying levels of success on Isla Sorna.

The male and female Tyrannosaurs moments before killing Eddie Carr.
A Tyrannosaur family was involved in both the Isla Sorna Incident of 1997 and the following San Diego Incident. Their involvement began when the son was taken from the parents by InGen Hunters Roland Tembo and his hunting partner Ajay Sidhu, who intended to use the infant as bait to lure the father, whom Tembo, a seasoned hunter, aspired to kill.[4] While the infant called for his parents to rescue, Peter Ludlow accidentally broke his leg while drunk, when he was startled by the sound of an animal moving through the undergrowth.[12]
After the Gatherers freed the dinosaurs captured by the InGen Hunters, Nick Van Owen discovered the infant T. rex. He decided to take him back to his team's mobile laboratory, where he and Dr. Sarah Harding mended the juvenile's leg. However, his parents arrived after first aid was applied, and began to corner the laboratory. Dr. Harding realized that the two Tyrannosaurs weren't exhibiting hunting behavior so she convinced her fellow Gatherers to hand the young T. rex to his parents.[4] Upon returning the infant to safety, the adult Tyrannosaurs returned to the mobile lab and began to push it over a cliff. However, Eddie Carr saved his fellow Gatherers from falling with the RV, but was promptly killed by the predators. Attracted by the smell of blood on Dr. Harding's shirt, the Tyrannosaurs parents traveled to the new camp of the Gatherers and the Hunters, and attacked the camp.[4]

The Buck, moments after being freed in San Diego.
While the Hunters fled, the female Tyrannosaur followed, killing many of them in the process. As the Tyrannosaur Buck continued his search, he was tranquilized by Roland Tembo (due to the fact that Nick Van Owen stole the bullets intended to hunt the dinosaur). After the female Tyrannosaur's attack, Peter Ludlow ordered the remaining InGen Hunters to secure the Tyrannosaur Buck and recapture the juvenile T. rex for Jurassic Park: San Diego. But his plan went astray when the Tyrannosaur Buck escaped confinement upon reaching San Diego, California and went rampaging throughout the city, killing several civilians.[4]
To stop the chaos, gatherers Sarah Harding and Ian Malcolm broke into Jurassic Park: San Diego to steal the baby Tyrannosaur so they use him to lure his father back into the docks. The plan worked, but when Peter Ludlow tried to recapture the juvenile, he was crippled by the Tyrannosaur Buck and finished off by the infant. The Tyrannosaur Buck's rampage ended when Dr. Harding tranquilized him before the San Diego police could shoot him. Both Tyrannosaurus father and son were reunited once more with the female when they were transported back to Isla Sorna.[4]
As a result of the San Diego Incident, Isla Sorna, and presumably Isla Nublar, were designated as restricted areas. In 1999 Dr. Wu secretly returned to Site B, and illegaly cloned several new dinosaurs. One of which was a Spinosaurus that managed to claim the north side of Isla Sorna as its territory.
Rescue of Eric Kirby (2001)

A T. rex was found by Dr. Alan Grant and a group of people during a rescue mission to Isla Sorna in 2001.
In 2001, Eric Kirby, a teenage boy marooned on the island from illegal sight-seeing, collected T. rex urine that he used to deter small carnivorous dinosaurs such as Compsognathus though he also learned that it attracted the island's intensely territorial Spinosaurus.[5] Weeks later, a male T. rex encountered a group of people led by Dr. Alan Grant, who travelled to Isla Sorna to rescue Kirby, while eating a Parasaurolophus.[13][5]

The male T. rex faces off against the Spinosaurus.
Grant tried to avoid the T. rex by standing still, but the Tyrannosaur noticed them and gave chase, bringing him into contact with the Spinosaurus. The two theropods sized each other up and began to fight. The Tyrannosaurus rex was the first to attack in the dual, biting down on the neck of the Spinosaurus and bringing it down to the forest floor. The Spinosaurus regained balance, however, and began to snap at his flanks. After the Spinosaurus swiped at him, the T. rex rammed his opponent head first, resulting in the Spinosaurus biting down on the T. rex's neck. As the Rex roared in agony, the Spinosaurus, with support from its arms, proceeded to snap its neck. The T. rex's body collapsed to the ground, nearly crushing Dr. Grant while escaping. The Spinosaurus then claimed the carcass of its fallen foe triumphantly.[5]
The Evolution of Claire (2004)
- "Well, if there is a queen of dinosaurs, it's probably her."
- —Bertie, describing the T. rex to Claire(src)
The original T. rex from Jurassic Park, dubbed "Rexy," was contained in a paddock near Main Street for Jurassic World. Her paddock was described as being densely packed with jungle growth, with a viewing booth on a transparent wall that overlooked the enclosure. She was normally fed live meat, typically goats as that was her preference, but once a month she was given meat mixed with amino acids and other nutrients to keep her healthy and strong; a flare was used for visual aid since she associated it with food. Her behavior was often withdrawn, which would be mistaken as shyness, but it was explained that she "decided [humans] need to earn her respect." She was considered wise, calculating, and curious.
Jurassic World (2005-2015)
- "We need more teeth!"
- —Gray Mitchell, inspiring Claire Dearing to release the T. rex on the Indominus(src)
On April 19, 2002, during the planning stages for the construction of a new park on Isla Nublar known as Jurassic World, Rexy was captured by an InGen security team led by Vic Hoskins.[14] The Tyrannosaur was placed in the T. rex Kingdom attraction, where she was intended to serve as one of Jurassic World's most popular animals once the park was open in 2005.[15] Though she was the only T. rex known to live in the park, there was a Cold Storage room for Tyrannosaurus rex present in the Hammond Creation Lab in the mid-2010s.[16]

Rexy smashes through the Spinosaurus skeleton prior to her fight with the Indominus rex.
The base genome of the Indominus rex, a genetically engineered hybrid that caused the second incident on Isla Nublar was Tyrannosaur.[6] During the hybrid's rampage across the island, Rexy remained in her enclosure.
The wreck of the Tyrannosaurus rex skeleton remained in the ruins of Jurassic Park's visitor center since the incident 12 years ago. Zach Mitchell used a rib from the skeleton along with a piece of the "When Dinosaurs Ruled the Earth" banner to make a torch when he and his brother Gray explored the place. The skull was later crushed under the weight of the Indominus rex's hand when it chased Owen Grady and Claire Dearing in the same area before being pursued by the JW001.
Rexy was eventually released by Lowery Cruthers under the orders of Claire, who lured it to fight against the Indominus. Smashing through the skeleton of a Spinosaurus, it roared threateningly at the Indominus, and the two began a vicious fight.
The two predators seemed evenly matched, however, the Indominus overpowered Rexy with her strong forearms. Just when the Indominus was about to finish her off, the Velociraptor Blue attacked the hybrid, allowing the veteran Tyrannosaur to overpower the Indominus, pushing it to the side of the Jurassic World Lagoon, where the park's Mosasaurus leaped from the water, and dragged the hybrid into the depths. Briefly looking at Blue, Rexy turned away and slowly made her way into the jungle.[6] Free on the island once more, she made her way to the top of the Jurassic World's control center, and roared triumphantly.[6]
Jurassic World: Camp Cretaceous (2016)
A mother-daughter pair was taken from Isla Sorna and placed in the jungle biome on the island Mantah Corp owned. The mother was nicknamed "Big Eatie" and the daughter was nicknamed "Little Eatie." They were at one point forced into fighting each other due to a BRAD tainting their food, and later Big Eatie was forced to fight a Kentrosaurus named Pierce.
Eruption of Mount Sibo (2018)
- "The T. rex would be dead by now, right?"
- —Franklin Webb.(src)

Rexy subdues a Carnotaurus during the eruption of Mount Sibo.
After the Indominus rampage throughout Jurassic World, Isla Nublar was once again abandoned to the dinosaurs, left to their own devices without human interference.
A few months after Jurassic World fell, Rexy attacked a group of mercenaries. One man is left on the ground and their helicopter lets down a rope ladder. They escape the Tyrannosaurus rex but the man on the rope ladder is swallowed by the Mosasaurus after it jumps into the air, and the Mosasaurus escapes from its pen into the ocean.[7]
Three years after the abandonment of the park, and two years after she messed with the mercenaries, Mount Sibo, the volcano which provided geothermal power to the original park, began to erupt, prompting Claire Dearing to organize a mission to rescue the dinosaurs from the doomed island.[7]

Rexy sleeping in transport truck.
At some point during the mission, in the midst of a stampede away from the eruption, Rexy attacked and fatally subdued a Carnotaurus, inadvertently saving Owen, Claire, and Franklin Webb.[7]
The Tyrannosaurus was later captured and, in a desperate attempt to save Blue, Claire and Owen had to get some of her blood. They found the Tyrannosaur and successfully got her blood but were locked in by some guards and Rexy woke up. As the agitated animal began to freak out and thrash violently, Claire escaped through the top and opens the main doors of the cage; Owen narrowly escapes the T. rex’s snapping jaws before she can bite him in half.[7]

The T. rex eating the remains of Eli Mills with the Carnotaurus

Tyrannosaurus roaring after killing Mills.
She was put into a cage underneath Lockwood Manor and, after nearly suffocating from a hydrogen cyanide leak, she was saved by being released by Maisie Lockwood into America. But before she leaves, Rexy suddenly reappears and snatches Eli Mills in her jaws, brutally shredding him before tearing him in half with a Carnotaurus, and ultimately devouring Mills, Rexy then knocked over the Carnotaurus with her head and the Carnotaurus got up and ran off. Then Rexy roared and walked away, crushing the I. rex fragment in the process and ensuring that no carnivorous hybrid could ever wreak havoc upon the world again.[7]
After she escaped, Rexy broke into a nearby zoo and roared at a male African lion, who stood his ground by angrily roaring back at her.[7] As the T. rex began to break into the zoo roaring at the male lion, the zoo's staff attempted to capture her. The T. rex bit at the rope carrying the cage by a helicopter before she managed to escape back into the forest.
Jurassic World: Dominion
Four years later, Rexy unintentionally attacked a drive-in movie theater as she was being chased by the Department of Prehistoric Wildlife. After three years, she was finally captured and taken to Biosyn Genetics Santuary.
During her first day in the sanctuary, Rexy attempted to eat a dead deer in the forest before the then-current apex, Giganotosaurus, interrupted. Their scuffle was short and ended with Rexy backing off, leaving the area and her meal to her opponent. After Lewis Dodgson's flaming giant locusts escaped the facility and set the forest on fire, Rexy was commanded to reach safety at the emergency zone. Rexy and the Giganotosaurus clashed once more, this time with the latter briefly killing the former. After a distraction from Kayla Watts, the Giganotosaurus fought the nearby Therizinosaurus. Returning to life, Rexy shoved the Giganotosaurus into the claws of the Therizinosaurus, impaling and killing it. The two then roared in victory after the fight. Sometime later, Rexy was met by two other tyrannosaurs, the Buck and Doe, who had also been in the valley prior to her arrival.[17]
Characteristics
Physical attributes
Tyrannosaurus rex cloned by InGen had fully scaled skin as juveniles and as adults,[4] when it is considered by scientists that Tyrannosaurus rex was feathered at least some parts of its body. The presence of feathers was seen in the naturally born individuals seen in the sequence taking place in the Cretaceous Period, where an adult Tyrannosaurus rex sports a short cape and mane of filamentous feathers across its back, neck, and shoulders. Its skin was thick, being able to offer some resistance to the razor-sharp toe claws of a Velociraptor,[2] and the sharp claws of the hybrid Indominus rex that were able to debilitate a full-grown Apatosaurus as well as the strong bite of the Indominus, which was able to crack the bulletproof glass of a Gyrosphere.[6] However, many of the adult Tyrannosaurs encountered by humans would bear at least one scar that would be found on their head or neck. Two adult males had a single scar on the side of their face.[4][5] The individual from Isla Nublar had several scars on her neck from a cloned Velociraptor that pounced on her.[6] According to evidence from the encounter between a Spinosaurus and a Tyrannosaurus rex on Isla Sorna, it suggests that the neck muscles of Tyrannosaurus rex could potentially be a vulnerable area. The Spinosaurus was able to successfully kill a Tyrannosaurus rex and nearly defeat another individual called "Big Eatie." Additionally, a Gigantosaurus was able to overcome an ancestor of the Tyrannosaurus rex. These instances indicate that the neck muscles of Tyrannosaurus rex may have been a weak spot, susceptible to attacks from certain predators.

A Tyrannosaur family unit on Isla Sorna in 1997.
Sexual dimorphism was present in the recreated Tyrannosaurus rex, such as the males having a throat wattle and much more prominent brows.[18] The males also had deeper vocalizations than the females[4][5], though the female T. rex of Isla Nublar also had deepened vocalizations when she got older.[6] Every adult Tyrannosaur encountered each had their own unique skin color and pattern. Males tended to have a green skin color and females tended to have a brown color while the juvenile known as Junior was a mix of the two aforementioned colors.[19]
According to founder and former CEO of InGen John Hammond, the cloned T. rex could run at speeds of 32 mph.[2] The clones seemed to have had an accelerated growth cycle as the Tyrannosaurus rex of Isla Nublar was the size of a 28-year-old when she was only five[15][11] and the only juvenile observed, Junior, was the size of a two-year-old tyrannosaurid yet was still highly dependent on his parents.[4]
In 2018, the Dinosaur Protection Group website uploaded an informative graphic for the "average" InGen Tyrannosaurus rex, with a length of 12 meters (39.4 feet, though this is commonly rounded up to a simple 40 feet in the franchise) and 7 tons (14,000 pounds).[20][21] However, one female specimen had grown larger, measuring over 13.5 meters (44.3 feet) long and standing over 5.5 meters (18 feet) tall.
Rexy, a late 20-year-old Tyrannosaurus rex, exhibited remarkable stamina and endurance as she pursued Claire relentlessly from the confines of her enclosure all the way to Main Street, where she encountered the decorative skeleton of a Spinosaurus. Despite sustaining injuries, Rexy valiantly engaged in a brutal confrontation with the ferocious Indominus rex. Surprisingly, her stamina did not falter even in the face of adversity. With the assistance of Blue, another dinosaur (Velociraptor), Rexy prolonged the fight against the Indominus rex until its eventual demise on Main Street. Following this arduous battle, Rexy managed to walk away, triumphantly leaving the scene.
Behavior
Unlike their prehistoric forebears, Tyrannosaurs bred by InGen were thought to hunt prey by seeing movement, likely considering stationary objects to be less of a threat.[2][4][5][6][22] This theory would be called into question during an incident on Isla Nublar where social media influencer Brooklynn tricked a T. rex into attacking a static cardboard cutout bearing her likeness. [23] From what has been observed of wild Tyrannosaurs, they were solitary animals, though a breeding pair on Isla Sorna roamed in the island in a pack.[5]

Both male and female Tyrannosaurs were fiercely protective of their infants.
Contrary to Robert Burke beliefs, supports the idea that Tyrannosaurs, including Tyrannosaurus rex, exhibited caring parental behaviors. Dr. Sarah Harding's theory, which aligns with current understanding, suggests that T. rex parents took care of their young. The offspring would remain in a nest while the parents provided food for them for approximately two weeks, until the juveniles were able to hunt independently.
While the exact number of eggs and young in a T. rex litter remains uncertain, it is known that if a T. rex baby went missing, the parents would actively search for it, relying on the cries of the missing offspring or the scent of its blood. However, if the parents were too far away to hear the calls, they likely relied on their territorial boundaries to protect their offspring within their home.
If Tyrannosaur parents detected the scent of their offspring's blood on a potential threat, they would confront and address the perceived danger. This behavior indicates a strong protective instinct and a willingness to defend their young.
The observations of family, like Big Eatie and Little Eatie provide evidence that mother and daughter Tyrannosaurus rex can remain together as a family, even when the daughter reaches a size comparable to her mother or close to it as sub adult. Despite uncertainties about the exact age at which Little Eatie would typically become independent, she still appears to rely on her mother for guidance. The limited environment they inhabit may contribute to the daughter's continued presence with her mother, as it may not provide sufficient resources or suitable conditions for her to venture out on her own. Little Eatie has demonstrated her strength by successfully defending herself against aggressive dinosaurs, but she also exhibits signs of fear when confronted with overwhelming numbers, prompting her mother to intervene and protect her.
In their interaction, Big Eatie and Little Eatie frequently partake in playful displays of aggression, emulating the semblance of a genuine fight. This behavior is characterized by vigorous cranio-facial biting and jovially pushing each other using their bodies. The aforementioned conduct, as witnessed during the interaction between Big Eatie, the maternal figure, and her daughter, is indicative of their spirited and lighthearted approach.
Tyrannosaurs reflected a high level of intelligence in several instances. The individual of Isla Nublar, in particular, has shown a good deal of intelligence during both the Isla Nublar incidents in both 1993 and 2015. In the former, she tested the electrical fences after the power outage, seemingly aware of the lack of power before attempting to escape.[2] During the incident in 2015, it showed enough intelligence not to attack Blue during and after their fight with the Indominus, aware of the key role the Velociraptor played in distracting the hybrid as it attempted to kill her.[6] Both the male and female Tyrannosaurus during the Isla Sorna Incident in 1997 also showed a high degree of intelligence, seen in their efforts to protect their infant from the humans, even going so far as to push a trailer over a cliff and hunt in a familial pack.[4]

In the late Cretaceous period, Tyrannosaurus rex was the ancestor of dinosaurs like Rexy, Buck, and Doe. These individuals were cloned from this ancient species. While the original Tyrannosaurus rex was likely a solitary creature, capable of living and hunting alone, it is interesting to note that if a pair of T. rex encountered a lone individual, they could potentially socialize with it and even accept it into their group, forming a pack. It is possible that Rexy, who had been living on Isla Nublar without any contact with her own kind for many years, may not have had the opportunity to learn how to interact aggressively or peacefully with other T. rex. This means that when she encountered Buck and Doe, who were also clones of the same species, there was a chance for a calm and non-hostile interaction. It's important to consider that a lone Tyrannosaurus rex might be aggressive towards others of its kind due to territorial or resource competition, or for the protection of their young. However, in Rexy's case, she did not have any territory, resources, or young to defend, which may have contributed to the peaceful encounter with Buck and Doe.
Behind the Scenes
Jurassic Park (1993)
Design

Early design concept by Tim Lawrence
Early design work for the Tyrannosaurus rex entertained ideas not present in the final film. One early concept Spielberg considered was to give the dinosaurs frog-like features to show their origin as genetic amalgamations. Artist Tim Lawrence created an early head sculpt with the basis coming from toads. This was never meant to be the final design, as certain features like teeth were omitted, but just a basis to test the ideas.
Mark "Crash" McCreery created the design of the T. rex that was used in the film. McCreery was working on Terminator 2: Judgment Day when the late Stan Winston moved him from that project to create sketches of the T. rex to generate interest in the film for Universal Studios.[24] His first drawing was the T. rex running against a plain white background as a motion study. His second was of the T. rex in a jungle setting lifting its left leg high in an attack stance reminiscent of a bird of prey.[25] McCreery created the designs without a reference to go by, creating the drawings with what he remembered in his mind of then-current information and new paleontological findings. After these sketches were done, Winston showed Steven Spielberg what McCreery had created and Spielberg gave his suggestions for the design of the animal. He felt that the design depicted in McCreery's drawings should have longer legs to hold the weight of it and that the feet were too small and bird-like. Spielberg also felt that the forearms looked weak.[24]
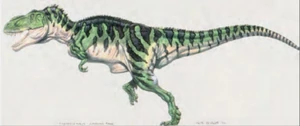
Character study by Mark Hallett from 1990.
Several paleoartists were contacted in 1990, notably to design the T. rex. Among those consulted were Mark Hallett, Gregory S. Paul, and John Gurche. As his first assignment from production designer Rick Carter, Mark Hallet created concept art of the T. rex breakout. Afterward, Hallett created concept art of the Tyrannosaur's attack on the explorers and then storyboards of the Tyrannosaur's attack from the driver's side view of one of the tour vehicles. Finally, he created a character study of the T. rex.[26] Concept art of scenes featured of the T. rex by Craig Mullins,[27] David Negron,[28] John Bell,[29] and Tom Cranham,[30] resemble Hallet's design. Paleontologist Gregory S. Paul created skeletal and muscle studies of the Tyrannosaurus rex to be used as the base form of the dinosaur.[31][32] Paleoartist John Gurche also did concept art of the T. rex, these concepts being its anatomy and reconstructions that were accurate for its time.[33] Paleontologist Dr. Robert Bakker sent the filmmakers diagrams of Tyrannosaurus rex teeth, but according to Bakker "the powers that be didn't like the real tooth shape" and used a different, inaccurate design for its teeth.[34] The eyes of the T. rex were kept party by director Steven Spielberg because he felt it looked better when she was running toward the camera.[35]

The second concept art made of Tyrannosaurus by Mark "Crash" McCreery.
Winston and McCreery would spend months redesigning the T. rex multiple times until a finalized design was reached.[24] When sculpting the 1/5 scale maquettes, Stan Winston and Mike Trcic spent time focusing on the design of the T-rex's head, with the maquettes going through over thirteen different head designs as according to Paul Mejias, "[The dinosaurs] had to be perfect."[36] Trcic created several anatomically accurate T. rex head sculpts as a potential design, but this would go unused in favor of a broader head and exposed front teeth.[37] According to Gregory S. Paul, Trcic also used one of Paul's T. rex skeletals when designing the T. rex,[38] but director Steven Spielberg and Stan Winston ordered the dinosaurs to receive alternations from the current scientific knowledge of the dinosaurs Paul created skeletals for to copyright their designs, even though Trcic wanted to strictly use Gregory S. Paul's diagrams.[39][31][38] However, Trcic has said that after many arguments with Winston over the design of the T. rex, the T. rex design was "60% where [he] wanted it to be." McCreery then created another design of the T. rex based on the maquette.[40]

Concept art of a design of the Tyrannosaurus by McCreery from 1991.
Early concepts of the T. rex depicted her as having a green coloration with black striping.[28][30][41] The final coloration of the T. rex chosen for the first film was a dark brown color. McCreery explained that the reasoning behind this was because an animal as large as T. rex would not need camouflage and that the team feared that too strong of coloration might make it look fake.[42] A green coloration would later be used for the males in The Lost World: Jurassic Park and Jurassic Park III. The design that "Crash" McCreery first created would later be colored and used in promotional material for Jurassic Park and its sequel The Lost World: Jurassic Park.
Portrayal
- Stop-motion to CGI
Originally, most of the wide shots of the dinosaurs were to be portrayed by go motion animation created by Phil Tippett.[43] With consultation from Mark Hallett,[44] Stefan Dechant had created digital animatics featuring a computer-generated T. rex, but these were replaced by the go motion animatics created by Tippett Studio.[45] An animatic was even created of the breakout sequence featuring the go motion T. rex. Tippit and his team sent Spielberg animation tests of Tyrannosaurus rex and Velociraptor. Though a motion blur was added to make the stop motion dinosaurs more realistic, Spielberg felt that the movements of the dinosaurs were still jerky. Dennis Muren then suggested to Spielberg that Industrial Light and Magic create computer-generated full-sized dinosaurs. Interested, Spielberg requested a test be made featuring CGI dinosaurs.[43]

The go motion Tyrannosaurus.
After ILM created a herd of Gallimimus skeletons running,[43] Steve 'Spaz' Williams with support and assistance from Mark AZ Dippe, his friend and confidant, created a running Tyrannosaurus rex skeleton during off-hours and in-between assignments at ILM. The reference he used for the skeleton came from page 341 of Gregory S. Paul's 1988 book Predatory Dinosaurs of the World.[46] Spielberg was not fully convinced to use CGI for the dinosaurs until ILM made more tests featuring a fully fleshed T. rex and said T. rex chasing a herd of fully fleshed Gallimimus.[43] This skin was rendered by Stefan Fangmeier.[47] Though the dinosaurs were to be now CGI in the film, the stop motion animatics and tests would be used as a reference for the animatronic dinosaurs.[48]
- Animatronics
A full-sized Tyrannosaurus rex animatronic was created by Stan Winston Studio for the filming of the dinosaur's breakout. Taking two years to make, the animatronic was the first animatronic to be mounted on a motion simulator to achieve gross body movements and at the time was the largest animatronic the studio ever produced[49] only being surpassed by the Spinosaurus animatronic created for Jurassic Park III.[50] Powered primarily by hydraulics,[51] a 1/5 scale telemetry device shaped like the dinosaur was used to provide the movements of the full-sized animatronic[48] with the eyes being radio controlled.[52] Another animatronic was also used for shots of its feet that was an underbelly on a rolling platform with hydraulic legs and tail.[52][53] Another prop was a separate head with extra detailing and added mechanics used for close-up photography.[52]
There had been plans to create a full-sized sleeping T. rex that was later conceived as a miniature when Stan Winston proposed to the studio that the money that was to be used for this animatronic be used to create the full-sized Tyrannosaurus rex instead until the sleeping T. rex was scrapped altogether.[54] Concept art was even created by "Crash" McCreery of this cut prop.[55] Stan Winston Studio also considered using a 1/5 scale rod puppet before the full-sized animatronic was conceived.[54] This concept would later be put to life for the sequel Jurassic Park III, but only as a test.[56] Speilberg had also originally wanted the animatronic Tyrannosaurus rex to be a freestanding and that was able to walk until it was discovered that it was impossible and he realized how impractical it would be.[57]
The animatronics were filmed on set at Warner Brothers Studio Stage 16.[58] For the filming of the attack sequence, the animatronic with legs [53][48] and the insert head were used. The insert head, in particular, was manipulated by a highly poseable hydraulic-powered crane as well as man-power.[59]
There were troubles while filming the scene as both the animatronics began to shiver due to their latex skin absorbing the rain,[48] requiring the crew to dry the animatronics down after every shot.[60] Filming also received a major setback when the head-turn cylinder of the full-sized animatronic broke, though this was quickly repaired.[61] Overall, shooting of the scene was finished four days ahead of schedule.[62]
In the original endings for Jurassic Park, one raptor was to be crushed by one of the falling skeletons while the other would either be moved and crushed to the jaws of the T. rex skeleton by Dr. Grant using a crane or by Hammond shooting the raptor.[63][64][65] Another ending would have also featured Hammond coming killing the first raptor with a bazooka while Dr. Grant used a crane to kill the remaining raptor-like one of the other ending.[66]The T. rex was even scripted to die like her novel counterpart at one point.[67] These endings and her death were scrapped from the film because Spielberg believed the T. rex to be the star of the film alongside the smaller Velociraptor.[64]
Phil Tippit worked with ILM in post-production to create the dinosaur input device or DID for short; an armature like that seen in go motion models that could be manipulated by Tippit and his team of stop-motion animators.[68] Out of the four DIDs created, two were for T. rex while other two were for the raptors.[69] The T. rex DIDs was only used for the road attack sequence while ILM created the rest of the shots featuring T. rex as Tippitt's team and ILM were originally going to work together until it was decided that both would be split into two teams.[70] The digital model for the T. rex received several changes from Spielberg that differed from the animatronic, these changes being a different arm length, larger and stockier feet, and a more streamlined jaw as well as adjustments to her eyes.[35] Years later, ILM would modify the T. rex model for lip-sync tests for the 1996 film Dragonheart.[71]
Vocalizations
The female roars were created from crocodiles, lions, alligators, dog, penguin, tiger, and elephant layered together.[72][48] Whale blowholes were also used looped to create the sound of the dinosaur breathing.[72] The sound of the T. rex as it kills the Gallimimus was simply Rydstrom's dog, a Jack Russell Terrier named "Buster",[73] playing with a rope toy.[43] The footsteps of the T. rex were of redwood trees being cut down and falling to the ground.[48] The iconic high-frequency "scream" originates from a baby elephant that Gary Rydstrom and his team recorded. It was only recorded once creating this sound and the team tried to get the elephant to create the sound again, but it refused to do so. Because of this, Rydstrom used the same elephant sound for each take.[74] This elephant sound was used for mid-range frequencies with an alligator's growl and tiger's roar added.[72]
The Lost World: Jurassic Park (1997)
Design
For the The Lost World: Jurassic Park, a female, male, and juvenile Tyrannosaurus were set to appear in the film. In the digital storyboards by Stefan Dechant the male was depicted as either yellow and gray or as the same color as the female.[75] John Rosengrant later devised the green color scheme for the male.[76] One such concept by Rosengrant was a colored version of the 1991 T. rex concept art for the first film.[77] Another color scheme applied to this same concept art would be widely used in promotional material for the film. Even though the Buck was given a different skin color to differentiate it from the female, Stan Winston Studio was concerned that this would be difficult to see in low-light conditions. So Shane Mahan began to manipulate images of the T. rex from the first film, creating a series of eight head designs that he sent to Speilberg. The design chosen by Speilberg featured larger brows, a scarred face, and a neck wattle.[18]
Joey Orosco created the concept art for the juvenile.[78] The juvenile went through many changes in his color scheme, such as one of his maquettes depicting him as brown,[79] another maquette depicting him as bright green,[80] and one paint scheme of his animatronic depicting him as a duller green.[81] However, evidence in the film and promotional photos of the animatronic suggest that Junior is actually a mix of brown and green.[82] The female also received a new skin color as well, her skin being lighter than the previous female that appeared in the first film.[19] However, promotional material depicted her as a darker brown and sometimes with a bluish tent to her head.
Portrayal
- Animatronics

The two animatronic adults created for The Lost World: Jurassic Park.
For close-up shots in the film, two animatronics were used primarily to depict the tyrannosaur parents using the armatures of the full-body animatronic and insert-head of the first T. rex, the female in particularly using the insert-head armature. Unlike the first full-sized T. rex animatronic, the animatronics for the parents was from head to mid-torso with arms and were mounted on rail powered dolly carts.[83] This was done because Stan Winston Studio discovered there was no need to make a full-sized animatronic like in Jurassic Park as the audience could only see the head and half the body. Furthermore, the carts provided more mobility and freedom when compared to the motion platform.[84] The most notable usages of the animatronics were when the parents approach the trailer and when they attack Eddie Carr.[85] Two animatronics were used to portray the juvenile. One was a mixture of hydraulics and cables used when he was laying on his side while the other was remote controlled and used when someone was carrying him.[85]
- From Pteranodons to San Diego
In one of the original endings for The Lost World: Jurassic Park, Pteranodon or Geosternbergia (then classified as a species of Pteranodon) were to attack the rescue helicopter at the end of the film.[86] While at his vacation home in the Hamptons for the Fourth of July, director Steven Spielberg suddenly saw an image in his mind of a boy looking out of his bedroom to see a T. rex drinking from the family swimming pool. Prompted by the image he saw, Spielberg changed the ending to what is seen in the completed film[87] and included the image he saw as the scene where the Buck approaches the house of young Benjamin and his family. In one concept of the T. rex being transported, it appears the mother was to be captured instead of the father as this T. rex is brown instead of green.[88]
Vocalizations
For the male, pigs and "weird Costa Rican mammals", mammals that Gary Rydstrom and his team recorded but never knew what their identities were, had a similar screech like the baby elephant used for the females and were used in place of the latter. The juvenile's vocalizations were of a baby camel crying for its mother.[86] The original T. rex roars were also reused for the female.
Jurassic Park III (2001)
The Replacement
In early logo designs for the film, Tyrannosaurus was to be featured like in the previous two films. Many of the logos had the same T. rex design used in the logos for the previous films, but there were different designs exhibited in the preliminary logos such as the T. rex with a more widened mouth,[89] the T. rex more upright and looking straight ahead,[90] and a full skeleton of T. rex roaring.[91] For Jurassic Park III, the filmmakers wanted to have another dinosaur to replace Tyrannosaurus from the previous two films[92] and searched through many candidates in the process.[93] Eventually Spinosaurus was chosen after Paleontologist Jack Horner suggested Spinosaurus to the filmmakers as a replacement[94] and from the discovery of a Spinosaurus skull during the pre-production of the film.[50]
During early development of the film, Stan Winston Studio created a 1/5 scale rod-puppet T. rex. They filmed this rod-puppet in forced perspective to create several tests to see if they could prove a concept that would work.[56] This rod-puppet would ultimately go unused in the film.
T. rex versus Spinosaurus

The Spinosaurus and Tyrannosaurus animatronics on set.
Director Joe Johnston created the famous Spino vs T. rex as an homage to Ray Harryhausen's go motion dinosaurs and wanted to recreate a modern version of those fights.[95] In one draft of the script the carcass the Tyrannosaurus was eating was a sauropod[96] when the actual prop used in the film is the Parasaurolophus carcass used in The Lost World: Jurassic Park repainted[97] and the carcass itself is left unidentified in the film.
For the battle, the animatronic of the Buck was refurbished.[98] Due to how powerful the mechanical Spinosaurus was, the Spino destroyed the Tyrannosaurus rex with one final blow that broke its neck which in turn caused its head to collapse, releasing hydraulic fluid that John Rosengrant described as being "almost like blood spewing". Rosengrant further described the destruction of the animatronic as "[A] really sad ending to a long night of shooting".[50] Over 20 seconds of footage of the fight, particularly of the animatronics, was cut from the film.[99] Despite this, a shot of the animatronic fight where the Spinosaurus slaps the Tyrannosaur was still present in the theatrical trailer.[100] For the CG T. rex, the model of the Buck from the previous film was reused as a basic framework, but when it was all finished, it was essentially a new model according to Tim McLaughlin.[101] New geometry was created for its surfaces so that it would work better in ILM's simulations. New animation controls were added as well that were up to date at the time the computer graphics were created for the film and the model's UV Maps were reworked, though originally the ones from The Lost World were to be used.[102]
Jurassic World (2015) and Fallen Kingdom (2018)

The Jurassic World CG model.
Jurassic World saw the return of the T. rex that appeared in Jurassic Park. Director Colin Trevorrow described the film "This is [the Tyrannosaur's] Unforgiven."[103] The T. rex model was created by Steve Jubinville and the director aimed to make the model look as close as possible to its design in the first film.[104] The Jurassic World Tyrannosaurus rex was made to look older by giving her the scars she received from the end of Jurassic Park as well as tightened skin. The T. rex was primarily portrayed with performance capture technology rather than life-sized animatronics.[103]

T. rex animatronics on set for Jurassic World: Fallen Kingdom
In Jurassic World: Fallen Kingdom, the Tyrannosaurus rex was recreated through a mixture of traditional animatronics and CGI.[7]
Dominion (2022)
Trivia
Cultural Impact
In popular culture, Tyrannosaurus rex has an iconic status shared by few other species, helped in no small part by the prominent role of the T. rex in all five films in the Jurassic Park franchise. The design of the Jurassic Park franchise's Tyrannosaurus rex is a notably popular way to depict T. rex in media.[105]
Mike Trcic expressed disappointment with the popularity of this design in an interview with Shannon Shea (who worked with Trcic on Jurassic Park). In the interview, he said regarding how popular the design had become, “Whenever I search Google images for a Tyrannosaurus Rex [sic], most of the art I see is based on the original JP Rex. It’s a shame that people just accept that somehow it IS what a T-Rex [sic] looked like. It’s limiting because unless someone can travel back 65 million years, how can anyone be completely sure?”[106]
The vocalizations that were created by Gary Rydstrom are also a popularly used sound effect. Jurassic World sound designer Al Nelson said regarding how famous its roars were in the films: "The T. rex is one of the most iconic sounds in all of film history. Every sound designer knows it. Almost any kid knows it. When you hear it, you're like 'That's the T. rex!'"[107]
Paleontology
Section for real-life paleontology
Like other tyrannosaurids, Tyrannosaurus rex had very short arms with only two fingers. Despite the limbs' size, each were able to bench-press about 400 pounds. Although these were probably nearly useless while hunting, its jaws were not: Tyrannosaurus rex has an enormous skull armed with teeth the size of bananas. Unlike the teeth of most theropods, the teeth of tyrannosaurids are very thick and capable of crushing bones and with a bite force of a minimum of 4 tons of force and probably more, crushing bone, ripping flesh, and bursting blood vessels of the victim. The skull and neck bones show that T. rex had the largest neck muscles of any meat-eating dinosaur. It probably used its strong neck to twist and pull off big chunks of meat that it grasped with its jaws while supporting the huge head. Tyrannosaurus rex could bite with extremely strong force - one fossilized skeleton shows that it crushed and swallowed the bones of a smaller plant-eating dinosaur while another shows a T. rex coprolite with the crushed frill of a Triceratops. Additionally, in Jurassic World: Alive, the Generation 2 Tyrannosaurus is referred to as Tyrannosaurus magnus, which scientists have considered a separate genus, Zhuchengtyrannus.[1]
A 2016 study suggested that T. rex probably didn't roar, but most likely cooed, hooted, and made deep-throated booming sounds like the modern-day emu.
Gallery
Images
Vocalizations
Appearances
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Holtz T.R., Brett-Surman M., Jurassic World Dinosaur Field Guide, page 126-127.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 Jurassic Park
- ↑ Jurassic Park: The Game: "T. rex Chase"
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 4.12 4.13 The Lost World: Jurassic Park
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 Jurassic Park III
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 Jurassic World
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 Jurassic World: Fallen Kingdom Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "JWFK" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "JWFK" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 8.0 8.1 The Tyrannosaurus, according to JurassicWorld.com, had lived on Isla Nublar for 25 years, so Tyrannosaurus was probably recreated around 1990 or before. This also means that it would have been 3 years old of age at the time of the Isla Nublar Incident of 1993.
- ↑

- ↑
 Image from the Masrani backdoor
Image from the Masrani backdoor
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Jurassic World director Colin Trevorrow as well as Industrial Light and Magic members Geoff Campbell and Steve Jubinville have stated that the T. rex from Jurassic World was indeed the same individual that appeared in Jurassic Park.
- ↑ The Lost World: Jurassic Park Deleted Scene
- ↑ CG Supervisor of Jurassic Park III Christophe Hery identifies the carcass as Parasaurolophus. Furthermore, the prop used is the carcass from The Lost World: Jurassic Park repainted.
- ↑ In the archived message "WEEK 3" of the Masrani backdoor Vic Hoskins writes about "staring a seven-ton predator in the eyes" in the first year of construction of Jurassic World, in which InGen Security was on Isla Nublar to defend the construction workers there. The only predator known on Isla Nublar that reaches this weight is Tyrannosaurus and since there was no other T. rex confirmed to have been on the island at the time of the 1993 Isla Nublar Incident, the creature encountered by Hoskins was the T. Rex on Isla Nublar.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 The article for the T. rex Kingdom on JurassicWorld.com says that the Tyrannosaurus that resides there has lived on Isla Nublar for twenty-five years. This is the only T. rex confirmed to have lived on Isla Nublar, so this individual is the same as her. This is further confirmed in a SlashFilm article discussing Jurassic World's performance capture and an interview with director Colin Trevorrow.
- ↑ Jurassic World - Inside the Hammond Creation Lab (HD)
- ↑ Confirmed by Colin Trevorrow that they are Buck and Doe.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, pp. 45-46
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Comparison between Rexy, (young and old) the Buck, the Doe, Junior (additional shot), and finally, the Jurassic Park III T. rex.
- ↑ https://jurassicpark.fandom.com/wiki/File:T-rex_dpg.jpg
- ↑ https://i.imgur.com/ENqkAof.jpg Jack Ewins clarifying the DPG graphic.
- ↑ Cohn, Paulette. (June 12, 2015) Jurassic World's Dinosaur Expert Talks Facts vs. Fiction (INTERVIEW). Biography
- ↑ A Beacon of Hope
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. Cinefex, 55, p. 48.
- ↑ The Making of Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 20
- ↑ Hallet, Mark. (Spring 2013) Sketch me a Spitter! Prehistoric Times Magazine, 105, pp. 47-48
- ↑ The Making of Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 7
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 The Making of Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 9
- ↑ The Making of Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 13
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 The Making of Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 10
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 Gregory S. Paul: The Full Autobiography Part 4. gspauldino.com
- ↑ Curriculum Vitae - Gregory S. Paul: Books, Articles, Abstracts & Other Projects. gspauldino.com
- ↑ Kartzman, Mark. John Gurche Interview Artzar (archived from the original)
- ↑ Kushner, David. (January 17, 2012) Meet the Scientists Who Make Science Fiction Believeable. Popular Mechanics.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 zbrushcentral.com - Interview: ILM on Jurassic World (February 3, 2016) Retrieved from http://www.zbrushcentral.com/showthread.php?198673-Interview-ILM-on-Jurassic-World
- ↑ Duncan, Jody. (December 15, 2012) Jurassic Park's T-Rex - Constructing a Full-Size Dinosaur. Stan Winston School, excerpted from The Winston Effect: The Art and History of Stan Winston Studio.
- ↑ Hallet, Mark. (Spring 2013) Sketch me a Spitter! Prehistoric Times Magazine, 105, pp. 48
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 Morales, Bob. (April/May 1999) The PT Interview: Gregory S. Paul Part I. Prehistoric Times, 35, p. 10. Retrieved from http://gspauldino.com/PTinterview1999.pdf
- ↑ Paul, Gregory S. (Fall 2013) A Little More On Jurassic Park. Prehistoric Times, 107, p. 46
- ↑ Michael Trcic Discusses Creating the Jurassic Park T-Rex. YouTube
- ↑ Hallet, Mark. (Spring 2013) Sketch me a Spitter! Prehistoric Times Magazine, 105, p. 49
- ↑ Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. Cinefex, 55, p. 73.
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 43.2 43.3 43.4 The Making of Jurassic Park documentary
- ↑ Hallet, Mark. (Spring 2013) "Sketch me a Spitter! An Artist Remembers Jurassic Park". Prehistoric Times Magazine, 105, pp. 49
- ↑ Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. Cinefex, 55, p. 52.
- ↑ Failes, Ian. (April 4, 2013) Welcome (back) to Jurassic Park. fxgudie.
- ↑ The Making of Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 137
- ↑ 48.0 48.1 48.2 48.3 48.4 48.5 Return to Jurassic Park: Making Prehistory
- ↑ The Making of Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 104
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 50.2 Duncan, Jody. (September 29, 2012) Jurassic Park III's T-rex Killer: Spinosaurus. Stan Winston School of Character Arts.
- ↑ Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. Cinefex, 72, p. 73.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 52.2 The Making of Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 31
- ↑ 53.0 53.1 The Making of Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 107
- ↑ 54.0 54.1 Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. Cinefex, 55, p. 72.
- ↑ Jurassic Park Topps trading cards: #84 - Sleeping Tyrannosaurus
- ↑ 56.0 56.1 JURASSIC PARK III T-Rex Rod Puppet Tests & More.
- ↑ Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. Cinefex, 55, p. 48.
- ↑ The Making of Jurassic Park by Jody Duncan, p. 106
- ↑ Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. Cinefex, 55, p. 76.
- ↑ The Making of Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 111
- ↑ Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. Cinefex, 55, p. 79.
- ↑ The Making of Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 112
- ↑ Return to Jurassic Park: Making Prehistory
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 The Making of Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 118.
- ↑ Sharpio, Mark. (1993, August) In the Shadow of the Dinosaurs. Fangoria, 27. Retrieved from http://www.jurassicworlduniverse.com/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/199308-fangoria-125.pdf
- ↑ Freer, Ian (October 8, 2014) Steven Spielberg And Special Effects. Empire.
- ↑ Nerdist Podcast - Episode 772: Kathleen Kennedy (December 16, 2015) Retrieved from http://nerdist.com/nerdist-podcast-kathleen-kennedy/
- ↑ The Making of Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 132
- ↑ Duncan, Jody. (1993) Beauty in the Beasts. Cinefex, 55, p. 58.
- ↑ The Making of Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 133
- ↑ Failes, Ian. (May 31, 2016) An Oral History of ILM’s ‘Dragonheart’ On Its 20th Anniversary. Cartoonbrew.
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 72.2 The Making of Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 144
- ↑ Buachann, Kyle. (June 9, 2015) You’ll Never Guess How the Dinosaur Sounds in Jurassic Park Were Made. Vulture.
- ↑ Sullivan, Becky. (April 13, 2013) Jurassic Bark: How Sound Design Changed Our Imaginations. NPR
- ↑ The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 26
- ↑ The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 47
- ↑ Mark “Crash” McCreery and John Rosengrant T-Rex artwork from The Lost World: Jurassic Park II icollector.com
- ↑ The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 25
- ↑ Making the 'Lost World'
- ↑

- ↑ Twitter@SWinstonSchool From concept art to the real thing (with a lot of hard work in between by amazing artists) #30daysofdinosaurs. (June 14, 2016)
- ↑



- ↑ The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, p. 46
- ↑ Duncan, Jody. (May 29, 2012) The Lost World Jurassic Park 2's T-rexs. Stan Winston School of Character Arts, excerpted from The Winston Effect: The Art and History of Stan Winston Studio.
- ↑ 85.0 85.1 Return to Jurassic Park: Finding The Lost World
- ↑ 86.0 86.1 Return to Jurassic Park: Something Survived (...and came to San Diego)
- ↑ The Making of The Lost World: Jurassic Park by Don Shay and Jody Duncan, pp. 71-72
- ↑

- ↑
- ↑
- ↑
- ↑ The Making of Jurassic Park III
- ↑ Return to Jurassic Park: The Third Adventure
- ↑ jp3.jurassicpark.com
- ↑ Berry, Mark F. (January 1, 2005) The Dinosaur Filmography, p. 172. (Google Books) Retrieved from https://books.google.com/books?id=KoeACgAAQBAJ&dq=joe+johnston+ray+harryhausen&source=gbs_navlinks_s
- ↑ Jurassic Park III film script: Scene 40: Int. Plane
- ↑ This can be proven due to it having exposed ribs like the dead Parasaurolophus made for TLW and has a greenish skin color with a dark green splotch on its back like the repainted later.
- ↑ Jody Duncan writes that the T. rex animatronic was simply one of the Tyrannosaurus built for The Lost World: Jurassic Park albeit refurbished. The identity of the TLW Tyrannosaur that was reused for Jurassic Park III is the Buck due to the presence of a scar on the side of its face, neck wattle, more prominent brows, and bearing dark yellow striping on its neck and upper back.
- ↑ Goldwasser, Dan. (July 9, 2001) Don Davis - Interview. Soundtrack.net.
- ↑ YouTube - Jurassic Park III (2001) Theatrical Trailer
- ↑ https://i.imgur.com/etUow3z.jpg Cinefex #87, pg. 37
- ↑ Deckel, Larry. (October 2001) Jurassic Park III: Bigger, Faster, Meaner. Cinefex, 87, p. 37.
- ↑ 103.0 103.1 Sciretta, Peter. (April 29, 2015) Original T. rex Returns in ‘Jurassic World,’ This Film “Is Her Unforgiven”. Slashfilm.
- ↑ Jurassic World stevejubinville.com.
- ↑ Dinosaurs. www.bbc.co.uk.
- ↑ Shea, Shannon. (June 11, 2015) How We Made The Iconic T-Rex of Jurassic Park. Filmschool Rejects.
- ↑ Making Tyrannosaurus Rex Sound. Youtube
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||